.png)
骨汤如何在钙含量低的情况下支持骨骼健康? 骨头汤的核心营养在骨胶原蛋白
How Does Bone Broth Support Bone Health Despite Low Calcium Content?
.png)
骨头汤的核心营养在骨胶原蛋白
当听说骨汤支持骨骼健康,尽管它的钙含量很低,大多数人得出结论,它的矿物质必须是非常具有生物可利用性的,因此很容易在体内消化、吸收和利用。考虑到“like feed like以形补形”,我们可能还会假设矿物质以最佳比例存在于骨骼构建中。相比之下,市场上骨骼形成补充剂通常含有大量难以吸收的钙,而没有充分补充骨骼形成所需的微量矿物质。毕竟,骨骼不仅仅是由钙构成的。事实上,骨骼是建立在胶原蛋白支架上的,这使得胶原蛋白成为肉汤中最重要的骨骼构建成分。

骨骼是建立在胶原蛋白支架上的,这使得胶原蛋白成为肉汤中最重要的骨骼构建成分
大多数人得出结论,它的矿物质必须是非常具有生物可利用性的,因此很容易在体内消化、吸收和利用。考虑到“以形补形”,我们可能还会假设矿物质以最佳比例存在于骨骼构建中。相比之下,骨骼形成补充剂通常含有大量难以吸收的钙,而没有充分补充骨骼形成所需的微量矿物质。毕竟,骨骼不仅仅是由钙构成的。事实上,骨骼是建立在胶原蛋白支架上的,这使得胶原蛋白成为肉汤中最重要的骨骼构建成分。
胶原蛋白是人体中最丰富的蛋白质,占人体总蛋白质的25%到35%,是构建健康骨骼、软骨、皮肤、动脉、眼角膜、胎盘以及身体几乎所有其他结构所必需的。人体中胶原蛋白的产生会减缓年龄和健康状况,导致皮肤、关节和骨骼变得干燥、不那么柔韧、变薄和虚弱。想想皮肤松弛、关节吱吱作响、骨质疏松症的骨骼。
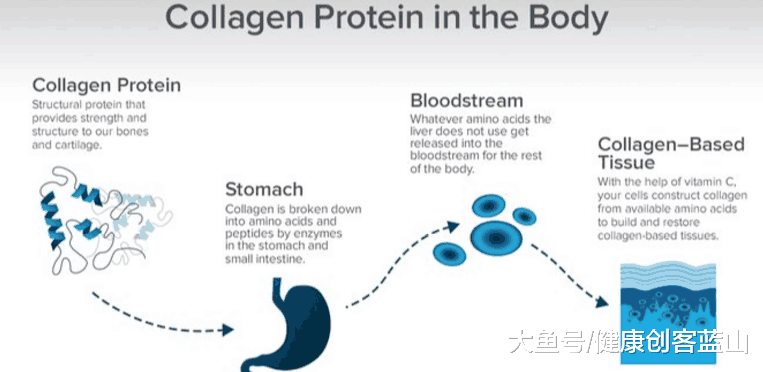
胶原蛋白是人体中最丰富的蛋白质,占人体总蛋白质的25%到35%
人体骨骼中含有50%到70%的矿物质和20%到40%的胶原蛋白,由胶原纤维构成。制作得当的骨汤不仅富含骨胶原,还富含附着在皮肤和软骨上的胶原蛋白。尽管在烹饪过程中胶原蛋白的巨大的三螺旋蛋白“变性”——也就是说分解——我们最终得到了大量的甘氨酸、脯氨酸和其他氨基酸,这些氨基酸是制造我们自己的胶原蛋白所必需的。脯氨酸和甘氨酸是健康胶原蛋白抗拉强度、弹性和保水能力的关键。尽管这两种氨基酸都被认为是“非必需的”氨基酸,但大多数人都无法生产足够的氨基酸,并从肉汤和其他富含脯氨酸和甘氨酸的食物中获益良多。因此,许多顶尖的研究人员认为这些氨基酸应该被认为是“有条件必需的”。
要造出好的骨头,首先我们需要胶原蛋白。骨骼的基本组成部分是胶原纤维,它形成一个网状结构,用来沉积磷酸钙和其他矿物质。胶原交联对于整个骨骼强度和抗骨折能力比矿物质水平和形态更重要。事实上,有些人的骨骼中含有丰富的钙和其他矿物质,这些矿物质在张力作用下会变得很弱,如未加固的混凝土。
例如,糖尿病患者可能患有骨质疏松症,不是因为矿物质密度低,而是因为他们的胶原蛋白被长期高血糖时产生的高级糖化终产物(AGES)破坏了。虽然这在糖尿病患者中最为明显,但任何患有低血糖、胰岛素抵抗和代谢综合征等血糖问题的人,年龄都会导致骨质减少和骨质疏松症。
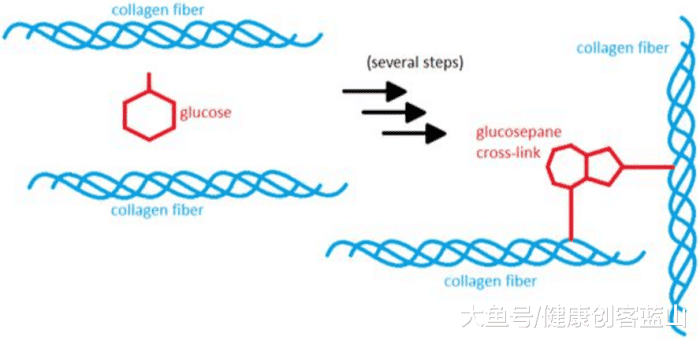
糖尿病者的胶原蛋白被长期高血糖时产生的高级糖化终产物(AGES)破坏了
大多数已经发表的胶原蛋白研究集中在骨关节炎上,但是米兰·亚当,布拉格风湿病研究所的DSci,在三年的时间里研究了120名骨质疏松症患者,并于1991年在兽孔医生发表了他的研究。他一半用钙,一半用水解胶原蛋白。骨分解产物中胶原蛋白和骨量的损失在水解胶原蛋白组明显低于钙组。最重要的是,胶原水解物显著降低了骨折的可能性。水解胶原蛋白是一种很容易溶于水的明胶产品,很容易用作食品补充剂和食品制造。它在常温下不会凝结,对食物的味道、气味或“口感”几乎没有影响。
1996年,亚当博士在《理疗学》杂志上发表了第二篇研究报告,涉及108名绝经后骨质疏松症患者,骨密度低于80%。他报道胶原水解物增强和延长降钙素的有益作用,改善骨代谢的整体标志物。降钙素是甲状腺分泌的一种激素,具有降低血液钙含量的作用。
2000年10月 CASE WESTERN RESERVE 大学的罗兰•莫斯科维茨医学博士, 在关节炎和风湿性关节炎研讨会上,报告他使用降钙素+胶原蛋白水解物比单纯用降钙素治疗骨关节炎和骨质疏松症效果更好。其高水平的安全性使其具有长期用于慢性疾病的吸引力。
显然还需要更多的研究,但是骨质疏松症已经威胁到全球2亿人,美国50岁以上的男性和女性有4400万,这些关于胶原蛋白的发现无疑是有希望的。
How Does Bone Broth Support Bone Health Despite Low Calcium Content?
Upon hearing that bone broth supports bone health despite its low calcium content, most people conclude that its minerals must be exceptionally bio-available and thus easily digested, assimilated and utilized in the body. Given that “like feeds like” we might also assume the minerals are present in optimum ratios for bone building. In contrast, bone-building supplements are often formulated with high levels of hard-to-absorb forms of calcium and without full complements of bone-building trace minerals. Bone, after all, is not built on calcium alone. In fact bone is built on a scaffold of collagen, making collagen the most important bone building component in broth.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, constituting between 25 and 35 percent of the body’s total protein, and needed for building healthy bones, cartilage, skin, arteries, corneas, placentas and just about every other structure in the body. Collagen production in the body slows down age and ill health, causing skin, joints and bones to become drier, less pliant, thinner and weaker. Think sagging skin, creaky joints and the brittle bones of osteoporosis.
Human bones contain anywhere from 50 to 70 percent mineral and 20 to 40 percent collagen, with collagen fibrils providing the structure. Properly made bone broth is rich in collagen not only from the bones but also from attached skin and cartilage. Although collagen’s giant triple-helix proteins “denature” — which is to say break down — during cooking, we end up with plenty of the glycine, proline and other amino acids needed to manufacture our own collagen. Proline and glycine are the keys to tensile strength, resilience and water-holding capacity of healthy collagen. Although both are considered “non essential” amino acids, most people cannot manufacture enough and benefit greatly from broth and other proline and glycine rich foods. Accordingly, many top researchers believe these amino acids should be considered “conditionally essential.”
To build good bone we need collagen above all. The basic building blocks of bone are collagen fibrils that form a latticework for deposition of calcium phosphate and other minerals. The collagen cross-links are more important for whole bone strength and fracture resistance than mineral levels and patterns. Indeed, some people have bones thick with calcium and other minerals that are weak and crack under tension like unreinforced concrete.
Diabetics, for example, may suffer from poor bones, not because of low mineral density but because their collagen is damaged by the advanced glycation end products (AGEs) created when blood sugar levels are chronically high. While this is most apparent in diabetics, anyone suffering from blood sugar problems such as hypoglycemia, insulin resistance and Metabolic Syndrome will have AGEs contributing to osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Most published collagen studies have focused on osteoarthritis, but Milan Adam, DSci, of the Institute of Rheumatism Research in Prague (1928-2008) studied 120 osteoporosis patients over a period of three years and published his research in Therapiewoche in 1991. He treated half with calcium and half with collagen hydrolysate. Loss of collagen and bone mass as seen in bone-breakdown products were significantly lower in the collagen hydrolysate group than in the calcium group. Best of all, collagen hydrolysate reduced the likelihood of bone fractures significantly. Hydrolyzed collagen is a gelatin product that is readily soluble in water, making it easy to use as a food supplement and in food manufacture. It does not gel at normal temperatures and has little effect on the taste, smell or “mouth feel” of foods.
In 1996, Dr. Adam published a second study in Therapiewoche involving 108 post-menopausal women with osteoporosis and bone mineral density lower than 80 percent. He reported collagen hydrolysate enhanced and prolonged the beneficial effects of calcitonin and improved overall markers of bone metabolism. Calcitonin is a hormone secreted by the thyroid that has the effect of lowering blood calcium.
In October 2000 Roland Moskowitz, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, reported his success with collagen hydrolysate for both osteoarthritis and osteoporosis in Seminars on Arthritis and Rheumatism He too found calcitonin plus collagen hydrolysate inhibited bone collagen breakdown better than calcitonin alone, making it “of interest as a therapeutic agent of potential utility in the treatment of osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Its high level of safety makes it attractive as an agent for long-term use in these chronic disorders.”
More research is clearly needed, but with osteoporosis a threat for 200 million people worldwide and forty-four million American men and women over the age of fifty, these findings on collagen are certainly promising.
Surprise! Research Reveals Little Calcium in Bone Broth https://www.thehealthyhomeeconomist.com/bone-broth-calcium/