科学家意外发现,绿茶可以杀死癌细胞
Green Tea Kills Cancer Cells, Scientists Accidentally Discover
你知道绿茶可以杀死癌细胞吗?来自印度和英国斯旺西的一组科学家直到最近才发现它。
想知道最好的部分吗?他们偶然发现了改变游戏规则的发现。科学家们喜欢把这种现象称为“幸福的意外”。
另一个值得注意的幸福事故包括微波炉。这将彻底改变未来大学生和单身汉们的生活。
不管怎样,回到茶的话题上。
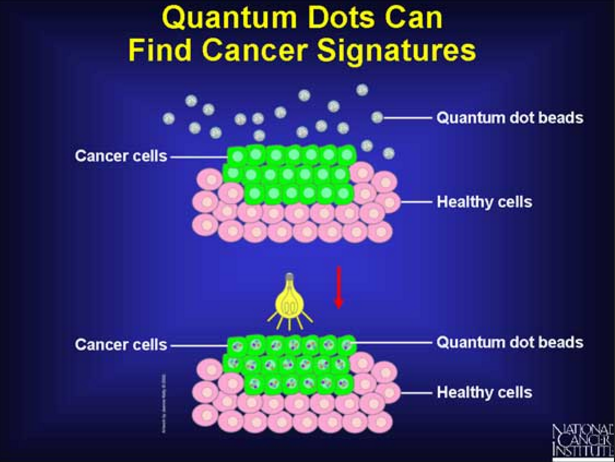
这一发现是在科学家们试图找到一种创造量子点的新方法时发现的。一种纳米粒子的大小只有人类头发的4000倍!
量子点的大小与人的头发和足球有关
量子点在技术和医学上都显示出很大的提升潜力。从改善电脑显示器的影像清晰度到现在对抗癌细胞。
但是,由于用化学方法制造量子点会产生一些有害的副作用,专家们正在寻找新的方法来制造量子点。
人们关注的焦点之一是寻找植物性的天然化学替代品。包括茶叶提取物的使用。
他们是怎么发现的
首先,科学家们将混合的茶叶提取物与硫酸镉和硫酸钠混合在一起,然后放置在培养基中。这个过程启动了微小量子点的形成,然后应用于肺癌细胞。
接下来发生的事情震惊了研究人员。量子点随后开始穿透癌细胞的纳米孔。造成80%的破坏。
一组科学家发现绿茶可以杀死癌细胞
一旦他们确认了结果,研究小组就发表了一份声明。首席研究员Sudhagar Pitchaimuthu博士说;“我们的研究证实了之前的证据,即茶叶提取物可以是一种无毒的替代品,而不是用化学物质制造量子点。”然而,真正令人惊讶的是,这些点积极地抑制了肺癌细胞的生长。我们没想到会这样。
慢点,伙计!在你吃完一加仑的绿色食物之前,先看看这个。在茶叶中淋浴还可以杀死癌症。
在接受BBC新闻采访时,Pitchaimuthu透露:“我们希望尽快开始现场实验室试验,如果一切顺利,大约两年后就会进行人体临床试验,所以也许十年后我们就能得到广泛的治疗。”
对于意外来说,这是个不错的发现。关于茶的其他好处,你可以看看我们的其他文章。
量子点(QUANTUM DOTS or QDs)的特点
量子点(QUANTUM DOTS OR QDs)是直径从2纳米到10纳米的半导体纳米晶体,由从II到VI或III到v的元素组成,由于其特殊的尺寸和表面效应,量子点是最有前途的纳米晶体之一,具有独特的光学和化学性质。与传统的有机荧光染料相比,量子点荧光染料具有许多优点,在光谱学方面具有许多优点,如荧光强度高、寿命长、耐光漂白等。基于量子点的多功能探针的亮度为同时进行癌症分子成像和靶向治疗提供了高灵敏度。在光谱应用方面,基于量子点的分子成像的灵敏度可以比常规荧光染料大2 - 3个数量级(表1),而且NIR- qds的近红外(NIR)荧光可以在深层组织中检测到,使其适合于高信背景比的体内成像
Green Tea Kills Cancer Cells, Scientists Accidentally Discover
by Chad Stan
May 24, 2018
green tea next to quantum dot
Did you know that green tea can kill cancer cells? Neither did a team of scientists from India and Swansea in the UK until they discovered it recently.
Want to know the best part? They stumbled on the game changing discovery by chance. A thing scientists like to call “a happy accident”.
Another notable happy accident includes the microwave oven. Something that’d completely change the lives of future college students and single guys everywhere.
Anyways, back to the tea.
The discovery was made whilst the scientists were trying to find a new way to create quantum dots. A type of nanoparticle 4000th the size of a human hair!
size of quantum dot in relation to human hair and football
Quantom dots show a lot of potential to raise the bar in both technology and medicine. From improving image definition in computer monitors, to now combating cancer cells.
But, because creating quantum dots chemically has some nasty and toxic side effects, experts are looking for new ways to produce them.
One focus has been on looking at plant-based natural alternatives to chemicals. Including the use of tea leaf extract.
How They Found Out
First, the scientists combined mixed tea leaf extract with cadmium sulphate and sodium sulphide, before being left to incubate. A process that kickstarts the formation of the tiny quantum dots, which were then applied to lung cancer cells.
What happened next shocked the researchers. The quantum dots then began to penetrate into the nanopores of the cancer cells. Resulting in an 80% rate of destruction.
team of scientists who discovered green tea kills cancer cells
Once they could confirm their results, the team released a statement. Lead researcher Dr Sudhagar Pitchaimuthu said; “Our research confirmed previous evidence that tea leaf extract can be a non-toxic alternative to making quantum dots using chemicals. The real surprise, however, was that the dots actively inhibited the growth of the lung cancer cells. We hadn’t been expecting this.”
Slow down though dude! Before you go and down a gallon of the green stuff, read this first. There’s more to showering in tea leaves to kill cancer.
When speaking to the BBC News, Pitchaimuthu revealed: “We hope to start live laboratory trials shortly, with human clinical trials following in around two years if all goes well, so perhaps in a decade we could have a widely-available treatment.”
Not a bad discovery, for an accident. For other benefits of tea you can check out our other articles.
https://spotmebro.com/news/green-tea-kills-cancer-cells-scientists-accidentally-discover/
ABOUT QUANTUM DOTS (QDs)
Characteristics of QDs for Biomedical Application QDs are semiconductor nanocrystals that range from 2 nm to 10 nm in diameter and consist of elements from groups II to VI or III to V. Given their special size and surface effect, QDs are one of the most promising nanocrystals with unique optical and chemical properties. QDs offer great advantages over traditional organic fluorescent dyes and present a number of beneficial characteristics for spectroscopy, such as high fluorescence intensity, long lifetime, and good resistance to photobleaching. The brightness of QD-based multifunctional probes affords high sensitivity for simultaneous cancer molecular imaging and targeted therapy. For spectrum application, the sensitivity of QD-based molecular imaging can be two to three orders larger than that of routine fluorescent dyes[31] (Table 1). Furthermore, the fluorescence in near infrared (NIR) of NIR-QDs can be detected in deep tissues, making them suitable for in vivo imaging with high signaltobackground ratio[17,18,23].
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3643664/
.png)
.png)
.png)