用于选择性癌细胞根除的过氧化氢酶调节的非均相Fenton反应:SnFe2O4纳米晶体作为治疗肺癌细胞的有效试剂
Catalase-Modulated Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction for Selective Cancer Cell Eradication: SnFe2O4 Nanocrystals as an Effective Reagent for Treating Lung Cancer Cells
过氧化氢酶 - 过氧化物酶是一种具有系统名称供体的酶:过氧化氢氧化还原酶. 该酶催化下列化学反应
供体+H2O2⇌氧化供体+ 2H2O
2 H 2 O 2 + O 2 + 2 H 2 O.
该酶是强过氧化氢酶,H2O2作为供体释放O2。
Catalase-peroxidase is an enzyme with systematic name donor: hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
donor + H2O2 ⇌ oxidized donor + 2 H2O
2 H2O2 ⇌ O2 + 2 H2O
This enzyme is a strong catalase with H2O2 as donor which releases O2.
摘要
非均相芬顿反应(Fenton reaction)已被证明是一种有效且有前途的选择性癌细胞治疗方法。
然而,该方法实现关键治疗选择性的关键工作机制仍不清楚。在这项研究中,我们首次提出并证明了过氧化氢酶(calalase)在实现非均相Fenton反应驱动的癌细胞治疗的治疗选择性方面发挥的关键作用。
非均相芬顿反应,其具有能够将H 2 O 2转化为高反应性羟基自由基的固体催化剂的晶格铁离子,可以有效地根除癌细胞。
在这项研究中,SnFe2O4纳米晶体,一种最近发现的优异的非均相Fenton催化剂,被用于选择性杀死肺癌细胞。内化到癌细胞中的SnFe2O4纳米晶体可以有效地将内源性H2O2转化为高活性羟基自由基,从而对癌细胞产生强烈的细胞毒作用。
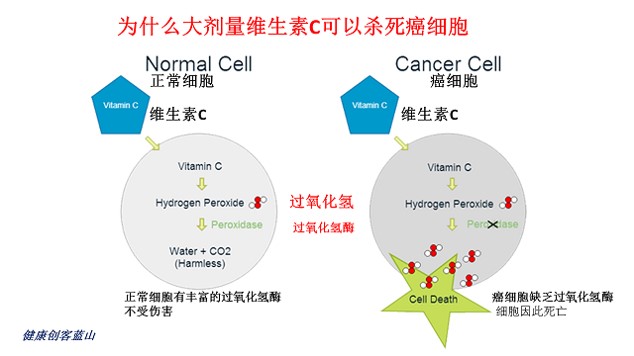
另一方面,正常细胞比癌细胞有更高的浓度的过氧化氢酶显着地可以阻止由内化的SnFe2O4纳米晶体诱导的凋亡细胞死亡。根据从体外细胞毒性研究获得的结果,通过存在正常生理水平的过氧化氢酶有效地抑制了相关的氧化攻击。
因此,证明SnFe2O4纳米晶体通过非均相Fenton反应影响凋亡的癌细胞死亡,并且对具有正常生理水平的过氧化氢酶的细胞是良性的。所涉及的异质芬顿反应的过氧化氢酶调节在实现异质芬顿反应驱动的癌细胞治疗的选择性癌细胞根除中起关键作用。
关键词:过氧化氢酶调节;非均相Fenton反应;过氧化氢;羟基自由基;肺癌细胞;选择性癌症治疗; SnFe2O4
Catalase-Modulated Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction for Selective Cancer Cell Eradication: SnFe2O4 Nanocrystals as an Effective Reagent for Treating Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
Abstract Image
Heterogeneous Fenton reactions have been proven to be an effective and promising selective cancer cell treatment method. The key working mechanism for this method to achieve the critical therapeutic selectivity however remains unclear. In this study, we proposed and demonstrated for the first time the critical role played by catalase in realizing the therapeutic selectivity for the heterogeneous Fenton reaction-driven cancer cell treatment. The heterogeneous Fenton reaction, with the lattice ferric ions of the solid catalyst capable of converting H2O2 to highly reactive hydroxyl radicals, can effectively eradicate cancer cells. In this study, SnFe2O4 nanocrystals, a recently discovered outstanding heterogeneous Fenton catalyst, were applied for selective killing of lung cancer cells. The SnFe2O4 nanocrystals, internalized into the cancer cells, can effectively convert endogenous H2O2 into highly reactive hydroxyl radicals to invoke an intensive cytotoxic effect on the cancer cells. On the other hand, catalase, present at a significantly higher concentration in normal cells than in cancer cells, remarkably can impede the apoptotic cell death induced by the internalized SnFe2O4 nanocrystals. According to the results obtained from the in vitro cytotoxicity study, the relevant oxidative attacks were effectively suppressed by the presence of normal physiological levels of catalase. The SnFe2O4 nanocrystals were thus proved to effect apoptotic cancer cell death through the heterogeneous Fenton reaction and were benign to cells possessing normal physiological levels of catalase. The catalase modulation of the involved heterogeneous Fenton reaction plays the key role in achieving selective cancer cell eradication for the heterogeneous Fenton reaction-driven cancer cell treatment.
Keywords: catalase modulation; heterogeneous Fenton reaction; hydrogen peroxide; hydroxyl radicals; lung cancer cell; selective cancer therapy; SnFe2O4
source:
Kuan-Ting Lee†¶, Yu-Jen Lu‡¶, Fwu-Long Mi§∥⊥, Thierry Burnouf#▽, Yi-Ting Wei†, Shao-Chieh Chiu⬡, Er-Yuan Chuang*#▽ , and Shih-Yuan Lu▲
† Technology Research Development Department, Plastics Industry Development Center, Taichung 40768, Taiwan (ROC)
‡ Department of Neurosurgery and ⬡Center for Advanced Molecular Imaging and Translation, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Tao-Yuan 33302, Taiwan (ROC)
§Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology, School of Medicine, ∥Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, ⊥Graduate Institute of Nanomedicine and Medical Engineering, College of Biomedical Engineering, #Graduate Institute of Biomedical Materials and Tissue Engineering, College of Biomedical Engineering, and ▽International PhD Program of Biomedical Engineering and Translational Therapies, College of Biomedical Engineering, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan (ROC)
▲ Department of Chemical Engineering, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu 30013, Taiwan (ROC)
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9 (2), pp 1273–1279
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b13529
Publication Date (Web): December 22, 2016
Copyright © 2016 American Chemical Society
*E-mail: eychuang@tmu.edu.tw.
Cite this:ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2, 1273-1279
Catalase-Modulated Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction for Selective Cancer Cell Eradication: SnFe2O4 Nanocrystals as an Effective Reagent for Treating Lung Cancer Cells - ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (ACS Publications) https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.6b13529
.png)
.png)