治疗心脏病和中风的纳米疗法-揭示炎症是导致心脏病和中风的根本原因
Nanotherapy for heart attacks and strokes
根据美国和荷兰的研究人员的最新实验,纳米颗粒可以减少动脉粥样硬化斑块的炎症。这些纳米粒子瞄准的是在斑块中存在的白细胞,可以用来治疗心脏病发作或中风的病人。
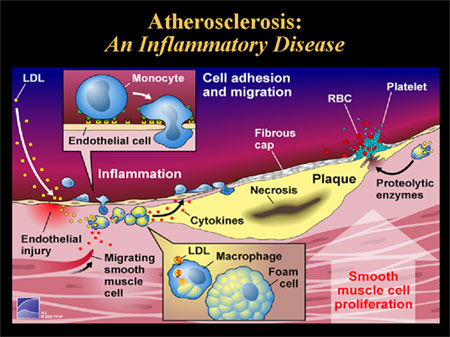
含有statin的HDL纳米颗粒可以减少斑块的炎症
动脉粥样硬化(Atheroscelerosis)或称为动脉硬化是一种炎症性疾病(An Inflammatory Disease),主要发生在大动脉中,是心脏病发作和中风的根本原因。白细胞在动脉斑块中积累。然后,它们分化成巨噬细胞(Macrophage),进一步加剧炎症,使病情恶化。
现在,纽约市西奈山医学院的Willem Mulder和波士顿、乌特勒支和阿姆斯特丹的同事一起研究发现,纳米颗粒可以靶向这些白细胞,并减少阻塞动脉的炎症。
纳米颗粒阻止巨噬细胞在阻塞的动脉中增殖
研究人员通过将降胆固醇药物辛伐他汀装入用于模拟高密度脂蛋白(高密度脂蛋白(HDL)或“好”胆固醇)的纳米颗粒中获得了结果。然后,他们将纳米颗粒注射到患有动脉粥样硬化的小鼠体内。这些动物患有这种疾病,因为它们缺乏蛋白质载脂蛋白E(Apolipoproteins E)(可以防止动脉粥样硬化),而且在实验前的几个星期里,他们已经吃了高胆固醇的食物。
由于体内成像、免疫学分析、分子生物学、放射化学和广泛的体内测试,穆德和同事们发现纳米颗粒阻止了巨噬细胞(Macrophage)在阻塞动脉中增殖。事实上,这种治疗在仅仅一个星期内就减少了斑块的炎症。这还不是全部:研究人员发现,随后的口服他汀类药物治疗和纳米治疗结合治疗 使斑块炎症持续减轻两个月。
纳米输送确保直接靶向
“我们的研究表明,抑制巨噬细胞的增殖可以用来抑制动脉粥样硬化斑块的炎症和治疗心血管疾病,”Mulder告诉nanotechweb.org,“而纳米 输送可以直接针对斑块巨噬细胞。”
在新的研究结果的刺激下,该研究小组表示,他们已经成功地扩大了纳米治疗技术,并将于本月下半月开始对大型动物(兔子和猪)进行实验。
https://s.click.taobao.com/w0OMXMw
Nanotherapy for heart attacks and strokes
Nanoparticles could reduce inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques, according to new experiments by researchers in the US and the Netherlands. The nanoparticles, which target the white blood cells present in the plaques, could be used to treat patients that have had a heart attack or stroke.
Statin-loaded HDL nanoparticles reduce plaque inflammation
Statin-loaded HDL nanoparticles reduce plaque inflammation
Atherosclerosis, or artery hardening, is an inflammatory disease that mainly occurs in large- to mid-sized arteries and is the underlying cause of heart attacks and strokes. White blood cells accumulate in arterial plaques. They then differentiate into macrophages that further exacerbate inflammation and make the disease even worse.
Now, Willem Mulder at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City together with colleagues in Boston, Utrecht and Amsterdam, have shown that nanoparticles can target these white blood cells and reduce inflammation in blocked arteries.
Nanoparticles stop macrophages in blocked arteries from proliferating
The researchers obtained their results by packing the cholesterol-lowering drug simvastatin into nanoparticles made from materials designed to mimic high-density lipoprotein (HDL or “good” cholesterol). They then intravenously injected the nanoparticles into mice suffering from atherosclerosis. The animals had the disease because they lacked the protein apolipoprotein E (which prevents atherosclerosis) and because they had been fed a high-cholesterol diet for several weeks prior to the experiments.
Thanks to a combination of in vivo imaging, immunological assays, molecular biology, radiochemistry and extensive in vivo testing, Mulder and co-workers found that the nanoparticles stopped macrophages in blocked arteries from proliferating. Indeed, the treatment reduced plaque inflammation within just one week. And that is not all: the researchers found that subsequent oral statin therapy combined with the nanotherapy supressed plaque inflammation for a further two months.
Nanodelivery ensures direct targeting
“Our work shows that inhibiting macrophage proliferation can be used to suppress atherosclerotic plaque inflammation and treat cardiovascular disease,” Mulder tells nanotechweb.org, “while nanodelivery ensures direct targeting to plaque macrophages.”
Spurred by on its new results, the team says that it has already succeeded in scaling up its nanotherapy technique and will be starting experiments on large animals (rabbits and pigs) in the second half of this month.
The present research is detailed in Science Advances doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1400223.
About the author
Belle Dumé is contributing editor at nanotechweb.org
Further reading
SQAd nanoparticles could help speed up stroke recovery (Nov 2014)
Nanoclusters act as antioxidants (Feb 2015)
Nanotube-loaded monocytes treat tumours (Apr 2014)
'Living' PEGylation could improve cancer therapy (Sep 2013)
http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/60803
.png)
.png)
.png)