Abstract
Dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane (DDT) is a known persistent organic pollutant and liver damage toxicant. However, there has been little emphasis on the mechanism underlying liver damage toxicity of DDT and the relevant effective inhibitors. Hence, the present study was conducted to explore the protective effects of vitamin C (VC) and vitamin E (VE) on the cytotoxicity of DDT in HL-7702 cells and elaborate the specific molecular mechanisms. The results demonstrated that p,p'-DDT exposure at over 10 µM depleted cell viability of HL-7702 cells and led to cell apoptotic. p,p'-DDT treatment elevated the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, induced mitochondrial membrane potential, and released cytochrome c into the cytosol, with subsequent elevations of Bax and p53, along with suppression of Bcl-2. In addition, the activations of caspase-3 and -8 were triggered. Furthermore, p,p'-DDT promoted the expressions of NF-百B and FasL. When the cells were exposed to the NF-百B inhibitor (PDTC), the up-regulated expression of FasL was attenuated. Strikingly, these alterations caused by DDT treatment were prevented or reversed by the addition of VC or VE, and the protective effects of co-treatment with VC and VE were higher than the single supplement with p,p'-DDT. Taken together, these findings provide novel experimental evidences supporting that VC or/and VE could reduce p,p'-DDT-induced cytotoxicity of HL-7702 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and NF-百B/FasL pathway.
Mentions
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a persistent organochlorine pesticide and a rodent hepatic tumor promoter for humans [1], [4]. Although there have been some literatures indicating DDT induced toxicity in liver and we have previously reported that DDT promoted the progression of liver cancer, few studies focused on the related specific mechanism involved in DDT's liver damage toxicity and the relative effective inhibitors. Therefore, in this study, we attempted to determine the effect of DDT on human normal liver cells and investigate whether there are preventive effects of VC and VE in plasma levels or not. Our study demonstrates, for the first time, that DDT exposure contributes to the elevated ROS content in HL-7702 cells, and ROS in turn serves as an activator helping to maintain NF-百B activation. Activated NF-百B complex binds to FasL promoter and causes robust increases in FasL levels in HL-7702 cells. Then FasL acts on Fas receptor to trigger caspase activation. At the same time, ROS induces the mitochondrial potential and contributes to the apoptosis. However, VC or/and VE supplement significantly counteract the ROS, thus eliminate the liver toxicology induced by DDT. These findings suggest VC or/and VE can reduce p,p∩-DDT-induced cytotoxicity of HL-7702 cells via the ROS-mediated NF-百B/FasL pathway and mitochondrial pathway (Fig. 10).
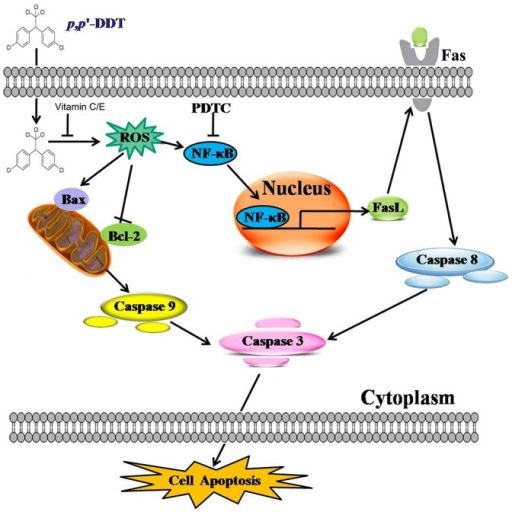
pone-0113257-g010: Proposed model of p,p∩-DDT-induced signaling pathways leading to apoptosis.ROS generation might play a critical role in the initiation of p,p∩-DDT-induced apoptosis of human liver cells through two mechanisms, one was the mitochondria-mediated pathway including elevation of ROS, decrease in 忖朵m along with the cytochrome c release from mitochondria into the cytosol, and activation of the caspase 9 and 3 in our previous study; and the other was the elevation of ROS, which resulted in the activation of NF-百B and expression of FasL, then triggered FasL-dependent pathway in the present study.