
ˇˇ
Difference Between Kinase and Phosphatase

Key Terms: Activity Regulation, ATP, Cell Signaling, Enzymes, Hydrolase, Kinase,
Phosphatase, Phosphotransferase
Main Difference ¨C Kinase vs Phosphatase
Kinase and phosphatase are two types of enzymes involved in the transferring of
phosphate groups between molecules. The main difference between kinase and
phosphatase is that kinase is a type of phosphotransferase that transfers a
phosphate group from the ATP to a substrate whereas phosphatase is a type of
hydrolase that removes phosphate groups from biological compounds. Both families
of enzymes are involved in the regulation of the activity of proteins by adding
or removing phosphate groups from proteins. The addition of a phosphate group to
a protein by a kinase may activate the protein while the removal of the
phosphate group from the protein may deactivate the protein. Most of these types
of regulated proteins act as enzymes. The regulation of the activity of protein
occurs based on external stimuli.
What is a Kinase
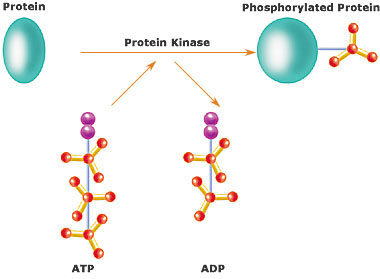
Kinase refers to an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from
ATP to a specific molecule. Therefore, kinases are the enzymes responsible for
the phosphorylation of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and
nucleic acids. The phosphorylation of proteins may activate the protein. This
activation of proteins is important in the cell signaling pathways since it can
be done in response to external stimuli. The phosphorylation occurs in tyrosine,
threonine, and serine residues of the protein. The phosphate group is obtained
from an ATP molecule. The phosphorylation of lipid molecules produce
phospholipids, which are the main components of a cell membrane. The
phosphorylated forms of inositol molecules serve as second messengers. The
addition of phosphate groups to nucleosides forms nucleotides, which are the
building blocks of both DNA and RNA. Carbohydrate kinases add phosphate groups
to simple organic molecules such as glucose and fructose. The general action of
a kinase on a protein is shown in figure 1.
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)
are two types of protein kinases. CDKs are important in the regulation of cell
division. Therefore, mutated CDKs may lead to the uncontrolled cell division in
cancers. Phosphatidylinositol kinases and sphingosine kinase (SK) are examples
of lipid kinases. Hexokinase and phosphofructokinase are carbohydrate kinases.
Nucleoside-phosphate kinase and nucleotide-diphosphate kinase are the two
kinases involved in the phosphorylation of nucleoside and nucleotides.
What is a Phosphatase
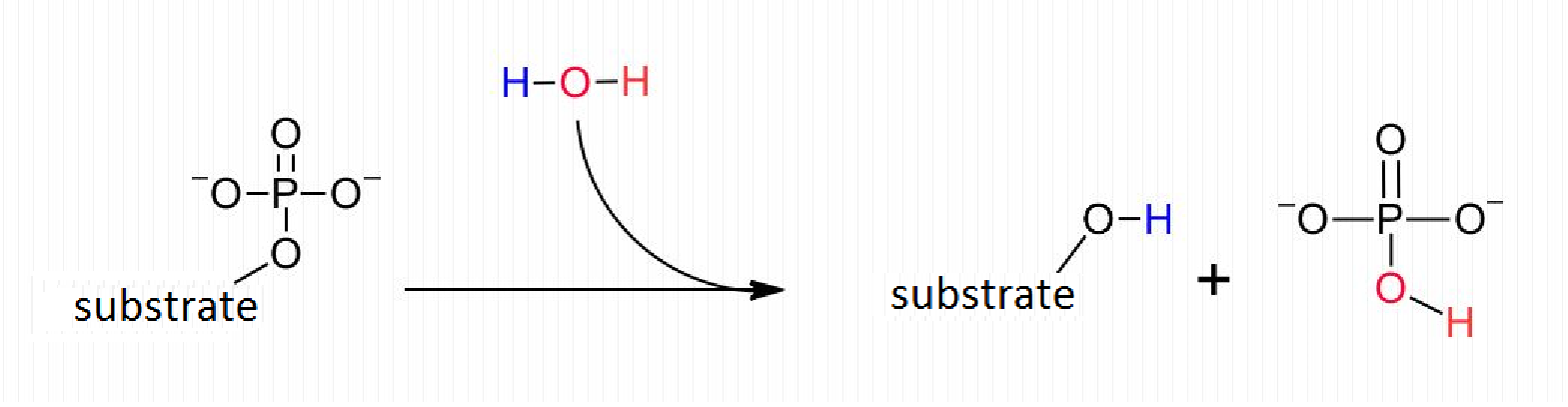
Phosphatase refers to an enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of organic
phosphates in an acidic or alkaline medium. Therefore, phosphatases are
responsible for dephosphorylation of biomolecules. Since phosphatases use water
molecules in order to add a hydroxyl group to the substrate, phosphatases are
categorized under the hydrolases family. The action of the phosphatases is the
opposite of the kinases. On that account, phosphatases are involved in the
deactivation of proteins in the cell signaling pathways. The removal of the
phosphate group may deactivate the protein. Both kinases and phosphatases are
also involved in the post-translational modifications of proteins. The general
action of the phosphatase enzyme is shown in figure 2.
PP2A and PP2B are two examples of protein phosphatases which regulate cellular
functions such as DNA replication, transcription, metabolism, and development.
Nucleotidases are a type of phosphatases that catalyze the hydrolysis of
nucleotides, forming nucleosides. They are important to maintain the balance
between nucleotides and nucleosides. Phosphatases are also involved in
gluconeogenesis, which produces glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors.
Similarities Between Kinase and Phosphatase
Both kinase and phosphatase are two enzymes that transfer phosphate groups
between molecules.
The action of both kinases and phosphatases are involved in the regulation of
the activity of proteins.
Difference Between Kinase and Phosphatase
Definition
Kinase: Kinase refers to an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate
group from ATP to a specific molecule.
Phosphatase: Phosphatase refers to an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of
organic phosphates in an acidic or alkaline medium.
Phosphorylation/Dephosphorylation
Kinase: Kinases catalyze phosphorylation.
Phosphatase: Phosphatases catalyze dephosphorylation.
Type
Kinase: Kinases are a type of phosphotransferases.
Phosphatase: Phosphatases are a type of hydrolases.
Additional Molecules
Kinase: Kinases use ATP to obtain phosphate groups.
Phosphatase: Phosphatases use water molecules to transfer hydroxyl groups.
Regulation of Proteins
Kinase: The addition of phosphate groups by kinases activates proteins.
Phosphatase: The removal of phosphate groups by phosphatases deactivates
proteins.
Examples
Kinase: CDKs, MAPKs, phosphatidylinositol kinases, and hexokinases are some of
the examples of the kinases.
Phosphatase: PP2A, PP2B, and nucleotidases are some examples of phosphatases.
Conclusion
Kinase and phosphatase are two types of enzymes that consist of opposite actions
on the phosphate groups. Kinases are a type of phosphotransferases that add
phosphate groups to the substrate from ATP molecules. However, phosphatases are
a type of hydrolases that remove phosphate groups from substrates. Kinases and
phosphatases are involved in the cell signaling pathways by activating and
deactivating various proteins respectively. The main difference between kinase
and phosphatase is the action of each enzyme inside the cell.
Reference:
1.ˇ°Kinase(s).ˇ± BPS Bioscience, Inc., Available here.
2.ˇ°Phosphatase.ˇ± Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Oct. 2017, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. ˇ°Ch4 kinasesˇ± By NIGMS ¨C Medicines by Design, National Institute of General
Medical Sciences (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. ˇ°General phosphatase mechanismˇ± By Lovinne ¨C Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via
Commons Wikimedia