��
Acute and chronic gastric ulcer gastritis:
Treatment with drugs and alternative means
bananas are not only a tasty fruit, but also a tasty medicine.
A natural flavonoid leucocyanidin present in unripe plantain banana pulp (Musa sapientum L. var. paradisiaca) protects the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions
http://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/17/9/1549?trendmd-shared=0
��
Alexey Portnov, medical expert
Last reviewed: 17.06.2019
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are ubiquitous, becoming increasingly relevant and prevalent. They become the most important problem, which requires an early and thorough solution. Diseases significantly limit the ability to work, lead to disability. In many cases, they have a lethal outcome. Gastritis tends to rejuvenate, it affects more and more young people. If the disease previously occurred mainly in large cities, megacities, now it affects the inhabitants of villages, villages, small towns on the periphery. Ulcerative gastritis can have serious consequences and complications, it is hard to treat.
Epidemiology
Ulcerative gastritis most often affects people over the age of 60 years. At the same time, women make up 65%, men - 78%. In children, gastric ulcer does not develop, gastritis occurs. In the ulcerative form, it overgrows after 16 years, under the influence of various adverse factors. Gastritis occurs in about 30% of cases. Approximately 50% of people suffer from chronic forms of gastritis. 80% of the people had at least one case of the disease.
Causes of the ulcerative gastritis
Gastritis has many different causes. The main reasons can be conditionally divided into two groups: those that are related to the characteristics of nutrition, and associated with lifestyle. Gastritis occurs as a result of malnutrition, non-compliance with diet. It can provoke stale foods, poorly prepared food, excessive content of food additives, dyes, preservatives, flavors and even spices. Gastritis can contribute to the constant use of too cold or too hot dishes. Negatively affect the stomach and marinades, sauces, dressings.
Stressful situations, busy schedule, constant snacks, lack of adequate nutrition, systematic refusal of hot (first) dishes. The cause may be smoking, alcohol abuse. The constant intake of medicines, especially antibiotics and non-steroid preparations, contributes to damage to the mucosa, resulting in the development of its inflammation. Often the cause is the infection of Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
Risk factors
In the risk group, first of all, people who do not observe the regime of the day and nutrition get to it. This is usually associated with hard work, a tight work schedule. Smoking, alcohol, the constant use of medicines, especially aspirin, and its derivatives, is an important risk factor.
Attention to their health should be treated by people who abuse fast food, snacking sandwiches. People who drink large amounts of coffee are more at risk of developing gastritis. If people avoid the use of hot, first courses, you can also refer them to the risk group.
The disease can arise as a consequence of a long stay in a stressful situation. If a person is constantly subjected to nervous and physical overload, the risk of developing gastritis increases significantly. Also, a person is more susceptible to gastritis if he has recently had an infectious, inflammatory disease. To risk factors include disorders of microflora, infection Helicobacter pylori.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is associated with morphological and functional disorders of the gastric mucosa. Ulcerative gastritis is accompanied by an increase in the amount of hydrochloric acid and its penetration into the lower, deeper layers of the stomach. Thus, ulcers are formed. An inflammatory process is formed around this site, which extends to both deep and surface layers.
Symptoms of the ulcerative gastritis
Ulcerative gastritis is regarded as a serious enough pathology of the stomach, during which rapid, rapid development of the disease occurs. The first signs make themselves felt after 5-6 hours, after the mucous membrane of the stomach has been exposed to irritating effects. First, there is severe pain in the stomach. At the person the appetite disappears, the general state of health worsens, the temperature raises. Then, nausea, vomiting with blood, bile is added. A persistent unpleasant aftertaste remains in the mouth. There is an unpleasant smell from the mouth.
Severe symptoms appear later. Constant strong pain in the stomach, constant vomiting, belching, flatulence, bloating. Vomit contains impurities of blood, mucus, and also consist of undigested food residues. When touched, painful sensations are observed. There may be spasms, less often - salivarily salivating.
First signs
The initial stage of the disease manifests itself in the form of severe pain in the stomach. Most often, the pain is sharp, cutting. Also painful are all areas around. All this against a background of nausea, vomiting. Also, unpleasant sensations in the mouth are added. As soon as you have the first signs of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor to make a timely diagnosis and take all the necessary measures.
Stages
There are three stages of the disease.
At the first stage there is hemorrhage, acute inflammation of the gastric membrane. The mucous membrane undergoes changes, microscopic changes take place on it. Gradually, small erosions are formed, which then develop into ulcers. The first defeat affects the antral department. There is an increase in hyperemia, edema. Peristalsis is sharply weakened.
In the second stage, acute ulceration occurs. Erosions merge, forming a massive ulcer. Usually the ulcer is irregular in shape. The bottom is uneven, constantly increasing in size.
At the third stage, there is a process of scarring, in which the convergence of the folds to the edges of the ulcer occurs.
Form
Acute gastric ulcer
An acute form of gastritis is not common. Mainly the chronic form prevails. The acute form is usually formed as a result of the ingestion of toxic substances, chemical preparations, strong medications on the mucous membrane. Often it is a consequence of the action of toxins, poisons. This is the main consequence of poisoning. Usually acute ulcerative gastritis results in recovery, which occurs a few days after the action of irritants has been eliminated. Indirectly to an acute gastritis can result or bring disturbance of a regimen of day, an overload of an intestine and a stomach. The acute form is most susceptible to people whose acidity of gastric juice is low.
The disease develops rapidly, rapidly. First of all, the surface layer is completely affected. In this case the deep layers remain intact. Inflammatory process lasts no more than 14 days, after which the erosions and ulcers begin to heal, to cicatrize.
Chronic ulcerative gastritis
The chronic form has its own characteristics. With this form, there are fewer lesions and associated pathologies. Characterized by a slow, measured flow. There are frequent relapses. The whole GI tract is affected, vomiting, nausea. Often there are bloody impurities. The aggravation occurs in autumn and spring. It is necessary to carefully follow preventive measures, to follow a diet. It is necessary to conduct preventive examinations during the period of exacerbation, undergo the necessary procedures, treatment courses. Causes are all the same causes that cause and acute form. In addition, it can be a consequence of repeatedly occurring acute gastritis. The culture of nutrition has no less influence. Negatively affects the irresponsible attitude to the choice of food, low quality food products, poor-quality cooking. Abuse of alcohol and tobacco can cause gastritis.
Erosive-ulcerative gastritis
It is one of the forms of acute gastritis, in which the normal functioning of the gastric mucosa is disturbed. There is a defeat of tissues, which are located much deeper. This form has its own specific features. For example, it is accompanied by the formation of numerous erosions, which gradually merge, forming erosion. Erosions damage the surface layers of the mucosa. They are much smaller in size than ulcers. Also ulcers are located more deeply. The first stage is the formation of erosion, in the second stage of erosion pass into ulcers.
To promote the development of this form, like any other, can stress, malnutrition, stress. This form can be a concomitant form in the defeat of the heart, circulatory system. The probability of the transition of this form to a chronic form is high.
Symptoms are more like a sharp form, which manifests itself 7-8 hours after the stimulus began to act on the mucous membrane. It is accompanied by a temperature and intense vomiting. It often manifests itself after a stressful effect.
Complications and consequences
Gastritis tends to become a stomach ulcer. This is the main complication, in which the mucous membrane corrodes, then this process affects the deep layers. Corroded stomach walls with hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice. The danger is that perforation can form. This hole in the wall of the stomach. Much bleeding can occur. This pathology arises unexpectedly, against a background of relatively normal well-being, without exacerbations.
The perforated ulcer is a dangerous pathology that is considered to be life-threatening. It is difficult to treat, almost does not cure. Danger of bleeding, which is almost impossible to stop.
Another dangerous complication is a tumor, which can be both malignant and benign.
Diagnostics of the ulcerative gastritis
Diagnosis is based on a clinical examination, as well as on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. On examination, the person's history is studied first, then they are interrogated, and the examination is performed. The main method is palpation, in which the stomach is felt. It is important to check soreness, neoplasm, and compaction in the stomach. The muscle tone of the stomach, the general condition of the gastrointestinal tract is assessed. However, only this data is not enough to make a diagnosis, so carry out additional studies.
Analyzes
In order to detect gastritis and diagnose it, it is necessary to conduct numerous studies. A clinical and biochemical blood test is performed, which can provide important information about the state of the stomach, the general state of the body. A general blood test shows the current inflammatory and infectious processes. Shows the number of blood cells, leukocytes. Important information can give the rate of blood sedimentation - ESR.
Biochemical blood analysis provides information on the chemical composition of the blood, can be used for differential diagnosis. Thus, a lower level of enzymes may indicate pancreatitis. If the protein appears in the blood, you can talk about autoimmune gastritis.
After that, blood samples taken from the gastric mucosa during the biopsy are examined. In addition, 2-3 tests are performed to identify the pathogen - Helicobacter pylori. Cytological and histological examination of biological material is carried out.
Instrumental diagnostics
Gastroscopy is the most effective diagnostic tool in gastroenterology. This is the method by which a special probe is inserted into the stomach, by means of which the digestive tract is inspected. It is used for examination of the upper sections of the digestive tract: esophagus, stomach, duodenum. If necessary, take photographs, which help to display the image on the screen. In the process of work, you can take photographs. There is also the possibility of taking biological material for research.
A pH meter can be performed. This is a relatively new procedure. During this procedure, the acidity of the gastric environment is determined. This has an important diagnostic value, since having indicators of acidity, you can determine the nature of the pathology. Based on the available data, it is also possible to differentiate gastritis from peptic ulcer. Also knowing the acidity, you can know exactly what type of gastritis develops. With erosive gastritis and with non-erosive gastritis, acidity sharply differs.
If necessary, conduct a daily pH-metry. To do this, a thin probe is inserted through the nose into the gastrointestinal tract, which contains electrodes that react with the gastric environment. A sensor is attached to the waist of the patient, which records the acidity.
An improved methodology has been developed and tested in many clinics. A person swallows a mini-capsule, after which it passes acidity indicators to the computer. For some time it remains attached to the wall of the stomach. Then, after a while, it is excreted outward with natural secretions.
Sometimes there is a need to determine the amount of Helicobacter pylori in the digestive tract, as well as in determining the state of microflora. To do this, examine the stool, stomach contents, tissues taken during a biopsy.
A respiratory test may be used. The patient drinks the juice in which urea is dissolved. With a high content Helicobacter pylori in the digestive tract, urea is split. This produces a large amount of carbon dioxide. The gas is released to the outside through the respiratory tract. By the gas concentration in the exhaled air, one can determine the nature of the pathology, as well as the quantitative parameters of Helicobacter.
Using the X-ray method, gastritis can also be diagnosed. But the effectiveness of this method is significantly lower than the informativeness of gastroscopy. It is less informative, inadequate. It is carried out with the use of contrast medium. However, with its help you can appreciate the relief of the stomach, its tone. You can confirm the diagnosis, or refute. On the x-ray, tumors are clearly visible. If a person has gastritis, it is difficult not to notice it, since the mucosa changes significantly. In order to finally confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct the test repeatedly, to track the results in dynamics.
With the help of ultrasound of the abdominal cavity it is possible to diagnose gastritis. Most often this method is used to determine chronic gastritis.
To diagnose it is enough to have a gastroscopy and ultrasound. If these methods are not enough, then only resort to other methods, such as X-ray, pH-metry, biopsy.
Endoscopic picture
In order to determine the presence of pathology, it is necessary to know the indices of the norm from which we proceed.
Normally, the mucosa of a pink hue, has a shine. The light that is falling from the apparatus is reflected. The surface is folded, the thickness reaches 0.5-0.8 cm. If the cavity begins to puff air, the folds straighten. In the output section, folds have a pale shade, their number is insignificant. In the area of the pylorus the folds are densified and round. As a variant of the norm, yellow color of the shell is allowed.
If a person has superficial gastritis, the mucosa becomes pink. Well expressed hyperemia, edema. Most often affects the antrum department. A vascular pattern is clearly visible. The walls can contain foamy mucus. The folds are tortuous, they do not straighten when inflated with air.
If a person has ulcerative gastritis, there are erosions and ulcers of various sizes on the mucous membrane. Erosions can merge with each other, forming ulcers. The edges of the ulcer have an uneven shade, bleeding of the edges is observed. Widespread hyperemia, hyperplasia, edema.
Differential diagnosis
��
First of all, it is necessary to differentiate gastritis from peptic ulcer, as they have a number of similar qualities. Also it is necessary to refute the usual functional disturbance of the stomach, for example: paknreatit, cholecystitis, stomach cancer.
A distinctive feature is that functional disorders can be hidden. In this regard, they are not easy to identify. In general, functional disorders are accompanied by dyspeptic disorders and severe pain. But these pains are quite long-lasting, noisy. In contrast to gastritis, in which the pain is acute, there are sharp, unexpected. In addition, functional disorders are accompanied by neurotic disorders. They are the ones that predominate in the clinic of the disease. Man quickly and excessively fatigued, his irritability, weakness greatly increases. Often the mood changes, sweating appears. You can clearly determine when exactly pain occurs, on which its intensity depends. For example, pain can be determined by the use of a certain product. These are the main distinguishing features of functional disorders that are not observed in gastritis.
Functional disorders of the stomach can be accompanied by vomiting, which develops according to the type of conditioned reflex and brings significant relief to the patient. With gastritis, vomiting does not bring relief, but only aggravates the condition, intensifies the pain and worsens the overall well-being.
The main method by which to determine functional disorders is gastroscopy.
Gastric cancer is sometimes difficult to distinguish from gastritis with a decreased secretory function. On the basis of clinical signs, it is difficult to diagnose cancer, so special studies should be carried out. It is especially difficult to distinguish these diseases in those patients who suffer from chronic gastritis for a long time. The main symptom of cancer is the appearance of persistent pain, which appears regardless of food intake. It is accompanied by excessive weakness, exhaustion, a perversion of appetite and a progressive decrease in body weight. In the early stages of palpation, the tumor can not be detected. It begins to feel in the late stages. In laboratory studies, an intensive reduction of hydrochloric acid in the composition of gastric juice, the appearance of atypical cells, and latent blood in the stool are found.
With a targeted biopsy with gastritis, mucosal atrophy and structural restructuring of the stomach are noted. With gastric cancer, filling defects are found, there are no folds of the mucous membrane, a change in the nature of the mucosa, the absence of peristalsis. With endoscopy, you can identify a cancerous tumor at an early stage. Surgical treatment in 90% ends successfully.
Differential diagnosis of gastritis and peptic ulcer disease
In order to choose the right treatment, it is important to differentiate ulcerative gastritis from peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. The peptic ulcer is characterized by intense pains that appear periodically, at a certain time. Most often after eating, at night, on an empty stomach. There is a significant relief after vomiting.
Gastroscopy and X-ray are used for differential diagnosis . The most accurate results are given by gastroscopy, X-ray is an auxiliary tool. With the help of these methods, it is possible to determine not only the localization of lesions, but also to assess the stage of the disease. The main difference is that gastritis affects the mucous membrane, and in case of peptic ulcer - the submucosa.
Who to contact?
Gastroenterologist
Treatment of the ulcerative gastritis
Ulcerative gastritis is treated exclusively with complex measures. Self-medication is extremely dangerous, can lead to serious complications and consequences. Usually, self-medication not only does not bring relief, but also provokes other, complex diseases, which quite often have a fatal outcome.
Complex therapy is a combination of drug treatment, alternative drugs, physiotherapy procedures, exercise therapy. A mandatory element of treatment is strict adherence to the recommended diet.
In the first days of exacerbation, complete starvation is necessary. This allows the digestive tract to reduce the degree of irritability, to come into a functional norm. You can drink only warm herbal decoctions and loose tea. It is allowed to use mineral water, non-carbonated. Carbonated water is prohibited. When choosing water, you should pay attention to the fact that it was intended for use in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and corresponded to an increased type of acidity.
From the second day it is recommended to include in the diet of mashed warm food. It should be boiled, sufficiently cooked. Good on the gastrointestinal tract mucous soups and milk porridge.
During periods of exacerbations, to ease symptoms and pain, herbal decoctions, alternative remedies, are used. They are also effective in the period of remission with a preventive purpose.
Medications
In the treatment of gastritis, various drugs and groups of drugs are used. To reduce spasm and pain, antispasmodics and painkillers such as no-chpa, spasmolgon, papaverine are prescribed. With increased acidity, prescribe drugs that block acids and alkalis, for example, gastrocepin. Effective antatsidy - Almagel, maaloks, renni. With reduced acidity, it is on the contrary increased, which makes it possible to achieve the correct functioning of the digestive tract. With strong and frequent vomiting, antiemetics such as motilium are used. In disorders of digestion and stool apply smectic (for diarrhea), dufalac (with constipation). In meteorism, carminative agents such as espumizan are important. At a gastritis of a bacterial etiology antibiotics are necessary. They are prescribed depending on which causative agent was the cause of the disease, and on the degree of contamination of the gastrointestinal tract with bacteria. If necessary, prescribe enzyme preparations (festal, mezim), antihistamines (suprastin, diazolone, cetrin). In exceptional cases, hormonal agents may be required.
If the patient bleeds in an easy degree, hemostatic therapy is needed, which makes it possible to adjust hemostasis. To do this, apply 100 ml of a solution of 5% epsilonaminocaproic acid. The solution should be drunk in small sips for 2 hours.
With reduced secretion of gastric juice, peritol is used as a syrup. To do this, apply 10-15 ml of solution every 4-6 hours.
With severe dehydration, depletion, and also when it is necessary to maintain the body at a stable level, use mafusol. It also has additional effects: it eliminates metabolic disturbances, normalizes the basic processes in the mucosa, eliminates the symptoms of endotoxicosis and replenishes the loss of blood. It is used for intravenous infusions in the amount of 800-1200 ml per day.
To increase local immunity, reduce the degree of ulceration of the gastric mucosa, use histodil 200 mg 3 times a day. The drug is administered intramuscularly, 5-7 days.
To stabilize cell membranes and increase the protective-regenerative potential of the body, intravenous administration of ascorbic acid, 70-200 ml of a 5% solution is recommended.
Vitamins
To maintain the normal functioning of the body, vitamins are used. It is recommended to take the following vitamins (indicated daily dosage):
Vitamin PP - 60 mg
vitamin H - 150 mcg
vitamin D - 45 mcg
vitamin K - 360 mcg.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
With ulcerative gastritis, cold is used to reduce pain, relieve spasms, stop bleeding. In some cases, heating may be indicated. To improve the assimilation of drugs, electrophoresis is used. Positive effects may have reflexotherapy, acupuncture.
Alternative treatment
In the complex treatment of ulcerative gastritis, alternative remedies have proven themselves well. They are used to reduce pain, eliminate symptoms. Also shown with a prophylactic goal in the period of remission. They give an opportunity to significantly extend this period. Alternative means are relatively safe. But they too can have side effects and contraindications. So, with the reception of some means of pain may increase, or open bleeding. Therefore, it is important to observe precautions. Before you start using any alternative remedy, you need to consult a doctor who will recommend how best to include it in the complex therapy.
With any ulcerative gastritis, the sea buckthorn has a positive effect. It promotes wound healing, erosion. Promotes recovery processes. It is used in the form of fruit pulp and oil. It is administered orally 5 ml, three times a day. It is recommended to apply before meals.
Cranberry juice makes it possible to reduce pain, promotes healing of mucous membranes, prevents inflammation. With regular intake of significantly increased acidity. It is recommended to take 15-20 ml three times a day, before meals. Also, cranberry syrup can be added to tea.
With high acidity and heartburn take the juice from the potato tubers. It is effective when taking half a glass twice a day. It is recommended to take before meals.
Herbal Treatment
When treating gastritis for a long time, flax seeds are used. To do this, take a tablespoon of flax seeds and pour them a glass of boiling water. Insist for an hour. You need to drink a decoction during the day.
Peppermint also has a positive effect. It can be drunk in the form of broth in small sips during the day. Cases of overdose are unknown. Applied at the onset of discomfort, such as nausea, pain. Also mint can be included in the composition of tea and drink during the day.
A good anti-inflammatory effect is provided by chamomile. It also reduces pain, spasms. In addition, it has a calming effect on the body. Chamomile is brewed in the form of a decoction. Approximately 10-15 grams of chamomile fill 2-3 cups of boiling water and drink during the day. You can also drink chamomile in the tea.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies are effective in the treatment of gastritis. The maximum their effectiveness is manifested when using complex treatment. There are practically no side effects. It must be remembered that many of them have accumulative effects, and therefore their effect may appear only after some time after administration, or after the completion of the full course of treatment. Precautions - it is always necessary to consult a doctor, since incompatibility with certain drugs is possible.
Collection number 1. With pain in the stomach
They take chamomile, a yarrow, and a three-dividing line. Mix with each other in equal parts. Prepare a decoction. Pour about 2-3 glasses of boiling water. Drink recommended 3-4 times a day, half the glass. It reduces pain painfully, eliminates spasms. It can be used after washing the stomach to restore normal microflora, removing the inflammatory process.
Gathering ��2. In the absence of appetite
It is recommended to prepare a decoction of bitter wormwood and a three-part watch. Take the plants in equal parts, pour boiling water. Apply about 15 ml before each meal.
Collection number 3. With ulcerative gastritis
It is necessary to prepare a mixture from the roots of ayr, marshweed and mushrooms medicinal. Take these plants in equal parts. Prepare a decoction that takes 1 tbsp before eating. An infusion of these herbs also proved to be very good. To prepare the herb, pour the herbs with vodka or alcohol, insist for 5-7 days, use the same as a decoction.
Collection number 4. With chronic gastritis
To prepare the broth, it is necessary to take the herb of St. John's wort, a thousand-acres, a mountaineer of poultry and peppermint in equal parts. Prepare a decoction, which after percolation is drunk half the glass 3-4 times a day.
Operative treatment
In acute necrotic processes, operations are carried out to remove part of the stomach. Vascular surgery may be required. In the presence of tumors, neoplasms produce their removal.
Diet with ulcerative gastritis
Treatment of gastritis is necessarily accompanied by the need to adhere to the correct diet, observe a diet. It is necessary to eat small portions, approximately 5-6 times a day. It is on this fractional treatment that most of the principles of GIT treatment are based. When treating gastritis, you must follow the treatment table number 1 and diet number 5.
In the diet it is recommended to include boiled, stewed dishes. Fried, smoked, baked 5 should be excluded completely. The food should be warm. Do not use hot or cold food. From any harmful products: fast food, smoked products, pickles, sweets, baked goods, sandwiches, should be completely abandoned. You can not also use semi-finished products and canned food.
It is necessary to include in the diet sour-milk products, yoghurts, cottage cheese. Meat is allowed only diet, boiled, for example: chicken breast, turkey, rabbit. Porridges need to be used a variety of, liquid, you can even rubbed. Good effect on the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract oatmeal, which envelops the walls of the stomach. Be sure to eat daily soups without frying. Recommended boiled fish, steam cutlets, boiled eggs, vegetable dishes. Shows not strong tea, herbal infusions, kissels, compotes. It is desirable to dilute the juices with water. Positively affects the broth of dogrose.
Exclude from the diet should be flour products, mushrooms and mushroom dishes, pasta, vegetables and fruits in raw form, spicy dishes. Do not use sauces, marinades, spices, spices. Coffee, kvass, cocoa and strong tea are also harmful.
Dishes with ulcerative gastritis
With ulcerative gastritis, despite numerous restrictions, food can be quite diverse. Of the products that can be eaten, and using the acceptable ways of cooking food products, you can prepare the following dishes:
broth from chicken / ideas / rabbit
broth with dumplings
broth with herbs
fish boiled / braised
cutlets, fish, steam
meatballs fish
soup with fish balls
fish pouring
Beef / chicken / turkey / rabbit boiled / stewed meat
chopped steak
meatballs meat
soup with meat balls
saut�� from stewed vegetables with meat
ragout of vegetables
vegetable soup
borsch without acidic components and tomato
Buckwheat / rice / wheat / millet soup
porridge semolina / oatmeal / pumpkin
porridge buckwheat / rice / millet / wheat / barley
mashed potatoes
salad from boiled grated beets
salad of grated carrots
braised cabbage
stewed eggplant, zucchini, pepper
pepper stuffed with dietary meat, stewed
eggplant / zucchini stuffed with stews
pepper stuffed with stewed vegetables
omelet, curd, cheese cakes
boiled boiled eggs / steep / stuffed
dairy and sour-milk products
cottage cheese with sour cream
fruit puree / souffl��
kvass, jelly, compote, juice, mors.
Menu with ulcerative gastritis
The menu looks something like this:
Breakfast - scrambled eggs, kissel
The second breakfast - semolina, or oatmeal porridge, mashed porridge, liquid soups. Tea (compote, kvass).
Lunch - soup, borsch, broth. Tea / juice / juice.
The second lunch - porridge or mashed potatoes, garnish - dishes from vegetables, meat, fish. It is recommended to drink a thick, enveloping consistency with a drink - jelly, etc.
Supper - oatmeal porridge / pumpkin / semolina, eggs boiled, compote / tea.
The second dinner - omelet / cheese cake / cottage cheese / fruit puree, tea / kissel / dairy products.
More information of the treatment
Products with gastric ulcer, gastritis, stomach pain: lung, breast, enveloping
Physiotherapy for chronic gastritis
Drugs
Treatment of gastritis with antibiotics: a scheme, how to take
Tablets from gastritis
Prevention
The main means of preventing gastritis is proper nutrition. At the same time, the power supply must be fractional. Also it is necessary to observe a diet. The food should be warm. Too hot and too cold food is a traumatic factor. Food should be chewed thoroughly. It is impossible to tolerate starvation, overeating. Methods of treatment should be gentle: cooking, baking, stewing, steaming.
It is necessary to minimize stress, neuropsychic overstrain. Eliminate bad habits. The use of alcohol and smoking after a previous gastritis is contraindicated. A sufficient level of motor activity is important.
It is important not to allow dysbiosis, to heal and provide prevention of bacterial, viral and parasitic infection. It is also important to prevent the concomitant diseases.
Forecast
Conservative treatment is effective in 77-80% of cases. Thus, out of 200 patients successful treatment is observed in 177 patients, which is 84, 5%, and in 23 people (11.3%) complications develop, bleeding. This requires additional surgical intervention. Surgical intervention is effective in 90% of cases
Ulcerative gastritis: symptoms, treatment, diet and nutrition, prevention | Competently about health on iLive
https://iliveok.com/health/acute-and-chronic-gastric-ulcer-gastritis-treatment-drugs-and-alternative-means_128275i15938.html��
BANANA FOR GASTRTIS
Among the products allowed for gastritis, bananas occupy an honorable place. This is the only fruit permitted for all forms of gastritis and ulcer. Bananas for gastritis - a source of substances useful for the digestive system: regenerating, healing, improving microflora and blood clotting. An unripe banana is used in South India as a bland diet for ulcer patients. Banana flour is often prescribed for dyspepsia in this part of the country. However, some studies show that bananas, because of their ability to increase the acidity of the stomach, are not recommended for gastritis and gastric ulcer.[1]
Diet for gastritis
Gastritis is dangerous because, in the absence of proper therapy, is aggravated by erosions and ulcers. Diet for gastritis is important along with drugs and includes foods that spare and restore the inflamed gastric mucosa.
The benefits and harm of bananas
Fruits occupy an important place in the diet of patients, but with different pathologies not the same fruits are recommended. Bananas for gastritis have many advantages, so that they are desirable in the menu of each patient. The benefits and harms of bananas are uneven. More benefits, it is that fruits are a dietary product and have the following properties:
Restore acid-base balance.
Remove toxins and poisons.
Help reduce the intensity of inflammation.
They act laxatively, but without diarrhea.
Improve the state of microflora.
Help relieve tension and stress.
Bananas contain resistant starch (RS) - this is a type of starch that is resistant to starch hydrolyzing enzymes in the stomach and thus behaves like dietary fiber. It has been proven that RS has a positive effect on disease prevention, including modulation of the glycemic index, the ability to lower cholesterol and weight control.[4]
Banana contains several biologically active compounds, such as phenolic, carotenoid, biogenic amines and phytosterols, which have antioxidant activity. [5]
Polyphenolic compounds found in bananas, such as hallocatechin, caffeic acid, cinnamic acid and catechin, have been shown to have antimicrobial activity (Chanwitheesuk et al. 2005; Shan et al. 2008), antioxidant (Chye and Sim 2009, Wong and Chye 2009), neuroprotective (Lu et al. 2005; Mandel et al. 2008), anti-cancer (Faried et al. 2007; Shankar and Mulimani 2007) and anti-proliferative properties (Jagan et al. 2008). [6]
Digestion depends on the method and time of their use. Along with heavy food, fruit lingers in the stomach and causes gas to form. If the stomach is well perceived such food, then eaten on an empty stomach, it will protect the mucosa and protects against the development of gastritis. If bananas cause flatulence, they are best consumed as a dessert, with a significant break after eating.
When used on an empty stomach, recommended to protect the stomach from increased acidity, discomfort and flatulence are possible. In order to avoid unpleasant feelings, eaten on an empty stomach bananas do not drink water or juice and limit their quantity.
At low acidity, ripe soft bananas are chosen and chewed them very carefully. Then the food mass is easier digested and absorbed by the stomach.Once scarce, and today the fruits available to all are firmly in our diet. Over time, it turned out that bananas are not only a tasty fruit, but also a tasty medicine. Bananas for gastritis are shown to all. In order for them to render the maximum benefit, the doctor must prescribe a method and mode of use, and the patient must strictly follow the diet and other doctor's prescriptions.
Bananas for gastritis: whether or not | Competently about health on iLive
https://iliveok.com/food/bananas-gastritis-whether-or-not_129170i16124.html��
Journal of Ethnopharmacology
Volume 65, Issue 3, June 1999, Pages 283-288
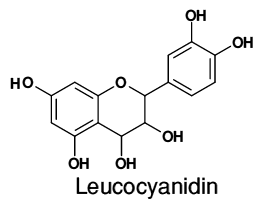
A natural flavonoid present in unripe plantain banana pulp (Musa sapientum L. var. paradisiaca) protects the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions
Author links open overlay panelDavid ALewisaWilliam NFieldsaGraham PShawb
a
Department of Pharmacy, Aston University, Gosta Green, Birmingham, B4 7ET, UK
b
School of Health and Sports Science, The University of North London, London N7 8DB, UK
Received 26 June 1998, Revised 30 December 1998, Accepted 7 January 1999, Available online 24 May 1999.
Abstract
The active anti-ulcerogenic ingredient was extracted from unripe plantain banana by solvent fractionation and identified by chromatography, spectroscopy and high performance liquid chromatography as the flavonoid leucocyanidin. Dried unripe plantain banana powder, the extracted leucocyanidin and a purified synthetic leucocyanidin demonstrated a significant (P<0.05) protective effect against aspirin-induced erosions.
A natural flavonoid present in unripe plantain banana pulp (Musa sapientum L. var. paradisiaca) protects the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions - ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874199000057��
Effects of hot-water extract of banana (Musa acuminata) fruit's peel on the antibacterial activity, and anti-hypothermal stress, immune responses and disease resistance of the giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbegii - ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1050464814001880��
Original research article
Synergistic effect of the combination of gallic acid and famotidine in protection of rat gastric mucosapanelK.AsokkumaraSaikatSenabM.UmamaheswariaA.T.SivashanmugamaV.Subhadradevia
a Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Paramedical Sciences, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
b Department of Pharmacy, Assam down town University, Guwahati, Assam, India
Received 25 May 2013, Revised 6 January 2014, Accepted 13 January 2014, Available online 26 April 2014.
Abstract
Background
Antioxidant supplements with existing drugs may confer better therapeutic efficacy in oxidative stress related diseases. The purpose of the present work was to characterize the interaction and investigate the protective effect of H2 blocker famotidine and gallic acid in combination against experimentally induced peptic ulcer.
Methods
Preventive effect of gallic acid and famotidine in different combinations was investigated against aspirin plus pyloric ligation induced ulcer in rat. Ulcer index, gastric juice volume, pH, other biochemical parameters of gastric juice and antioxidant activity using stomach tissue were estimated.
Results
Pretreatment with gallic acid and famotidine in combinations for 7 days, protected the gastric mucosa significantly (p < 0.05, 0.01), which was evidenced by decrease in ulcer index, gastric juice volume, free and total acidity, total protein, pepsin and DNA content, and increase in pH, carbohydrates concentration in gastric juice. Combination treatment increases levels of superoxide dismutase, catalase, reduced glutathione, glutathione reductase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and decreases lipid peroxidation, myloperoxidase in stomach tissue. Along with higher dose combination, lower dose combinations like gallic acid (50 mg/kg) plus famotidine (10 mg/kg) also offered better antiulcer activity than their individual effect. Histopathological studies confirmed their antiulcer activity.
Conclusion
Combination treatments confer synergistic protective effect against peptic ulcer in rats, which was related to the gastroprotective, antisecratory and antioxidant activity of combination treatment. Results proved that use of gallic acid with existing antiulcer drug will be more useful in the prevention/management of peptic ulcer.A natural flavonoid present in unripe plantain banana pulp (Musa sapientum L. var. paradisiaca) protects the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions - ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874199000057��
Pharmacognosy Res. 2011 Oct-Dec; 3(4): 232�C238.
Indigenous anti-ulcer activity of Musa sapientum on peptic ulcer
P. Prabha, Thirunethiran Karpagam,1,* B. Varalakshmi,1 and A. Sohna Chandra Packiavathy
Author information Article notes Copyright and License information Disclaimer
PG and Research Department of Biochemistry, PRIST University, Thanjavur - 614904, India
1Department of Biochemistry, Shrimati Indira Gandhi College, Tiruchirappalli-620002, Tamilnadu, India
Address for correspondence: Mrs Thirunethiran Karpagam, Department of Biochemistry, Shrimati Indira Gandhi College, Tiruchirappalli-620 018, Tamil Nadu, India. E-mail: moc.oohay@nagurum_magaprak
Abstract
Background:
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD), encompassing gastric and duodenal ulcers is the most prevalent gastrointestinal disorder. The pathophysiology of PUD involves an imbalance between offensive factors like acid, pepsin and defensive factors like nitric oxide and growth factors. The clinical evaluation of antiulcer drugs showed tolerance, incidence of relapses and side-effects that make their efficacy arguable. An indigenous drug like Musa sapientum possessing fewer side-effects is the major thrust area of present day research, aiming at a better and safer approach for the management of PUD.
Material and Methods:
The unripe plantain bananas (Musa sapientum) were shade-dried, powdered and used for phytochemical analysis and as antiulcer drug. In our present study Group I rats served as control and were treated with saline, Group II was indomethacin-induced ulcerated rats, Group III received aqueous extract of Musa sapientum along with indomethacin and Group IV received esomeprazole along with indomethacin for 21 days. The anti-ulcerogenic activity was investigated by performing hematological, mucosal, antioxidant profile in comparison with the standard drug esomeprazole.
Results:
Our findings from High - Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) analysis showed that Musa sapientum has an active compound a monomeric flavonoid (leucocyanidin) with anti-ulcerogenic activity. Results were expressed as mean �� SD. All our results are in congruous with the results of standard drug esomeprazole.
Conclusion:
It could be clearly concluded that administration of the aqueous extract of Musa sapientum at the dose used in this study tends to ameliorate ulcers. Its use in indigenous medicine should be scientifically scrutinized with further research.
Keywords: Esomeprazole, gastric mucosa, leucocyanidin, Musa sapientum��
RESULTS
��
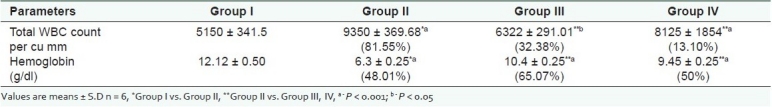
There was a significant decrease in the body weight (100%) in the ulcer induced group when compared to normal. Treatment with herbal drug of Musa sapientum (200%) and standard antiulcer drug esomeprazole (57%) showed a significant weight gain.
There was increase in the gastric volume (160.33%), (P < 0.001) and decrease in pH (51.61%), (P < 0.001) in the indomethacin administered group. On administration of Musa sapientum and esomeprazole, the level of gastric volume was significantly reduced (46.03%, 34.92%) and the pH was increased (93.33%, 76.66%) when compared to indomethacin-induced rats [Table 1].��
The gastric mucosal protein was significantly reduced (41.33%) in ulcerated rats when compared to normal. Treatment with Musa sapientum and esomeprazole significantly increased (60%, 41.81%) the mucosal protein when compared to the indomethacin administered group of animals. The gastric mucosal sialic acid was also significantly reduced (45.80%) in ulcerated rats when compared to normal. Treatment with Musa sapientum and esomeprazole significantly increased (62.34%, 42.25%) the mucosal sialic acid in indomethacin-induced ulcerated rats. Also, the level of mucosal hexosamine was significantly reduced (18%) in ulcerated rats when compared to normal. Treatment with Musa sapientum and esomeprazole significantly increased (13.4%, 11%) the mucosal hexosamine in indomethacin-induced ulcerated rats.
The nitric oxide in the gastric mucosal tissues was significantly decreased (27.84%) in ulcerated rats when compared to normal. Treatment with Musa sapientum and esomeprazole significantly increased (34.96%, 24.06%) the mucosal tissue nitric oxide in indomethacin-induced ulcerated rats. The nitric oxide in the serum was significantly increased (45%) in ulcerated rats when compared to normal. Treatment with Musa sapientum and esomeprazole significantly decreased (26.79%, 20.68%) the nitric oxide in the serum in indomethacin-induced ulcerated rats [Table 3].��
DISCUSSION
Peptic ulcer is a common disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.[19] Antiulcer drugs are associated with severe side-effects.[20] Clinical research has confirmed the efficacy of several plants for the treatment of gastroduodenal diseases.[21] Preliminary phytochemical screening of unripe plantain banana (Musa sapientum) revealed the presence of primary and secondary metabolites. Screening of active compound using HPTLC revealed the presence of a monomeric flavonoid Leucocyanidin.
Studies by David et al.,[22] reported that Leucocyanidin and its synthetic hydroxyl ethylated and tetra allyl derivatives were found to protect the gastric mucosa from aspirin-induced erosions. Leucocyanidin and its hydroxyl ethylated and tetra allyl derivatives significantly increased mucus thickness.
The mechanism by which indomethacin induces ulcer is by inducing H+ / K+ ATPase in gastric parietal cells. This increases the gastric acid secretion and decreases pH in ulcerated rats, whereas esomeprazole, a PPI (proton pump inhibitor) inhibits H+ / K+ ATPase in gastric parietal cells.[23] In our present study the decrease in gastric volume and increase in pH in Musa sapientum-treated animals might be by inhibiting the Hcl secretion. Amr et al.,[24] in their studies reported that there was significant decrease in gastric volume and increase in pH when the ulcerated rats were treated with Cinnamon and Chamomile in dose-dependent manner. Our results are comparable with their report. The decrease in the level of hemoglobin might be due to internal bleeding in the lesions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and increase in the count of WBC might be the function of immune cells against the inflammation in ulcerated rats. In Musa sapientum-treated animals the results were reversed which might be due to the presence of a flavonoid leucocyanadin, a compound which protects the gastrointestinal mucosa from lesions produced by various drugs like NSAIDs and other ulcerogenic agents, and was in agreement with the results of standard drug esomeprazole. Green unripe plantains have been reported to have an active principle(s) which enhances the formation of red blood cells in addition to the gastro-protective capacity against indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats.[25] David et al.,[26] in their study stated that dried unripe plantain banana powder, leucocyanidin extracted from Musa sapientum and a purified synthetic leucocyanidin have a protective effect against aspirin-induced erosions. Our results are in agreement with their report.
The decrease in the protein content of the gastric mucosa in the indomethacin administered groups may be due to damage in the gastric mucosa which results, in the leakage of protein into the gastric juice. Treatment with Musa sapientum increased the mucosal protein which indicates its ability to act at the cellular level in the mucus gland, i.e. it enhances cell proliferation and stimulates the growth of the gastric mucosa. This stimulatory effect of banana on mucosal growth was responsible for the rapid healing of ulcers in rats treated with indomethacin and was congruent with the results of esomeprazole. Musa sapientum increases mucus resistance to ulcerogenic substances thus enhanced the recovery from ulcers.[10]
There was a significant decrease in the levels of glycoproteins, viz. sialic acid and hexosamine, of the gastric mucosa in the ulcerated group of rats when compared to normal groups which might be due to damage in the mucosal layer. On treatment with antiulcer standard drugs (esomeprazole) and Musa sapientum, there was significant elevation in the level of sialic acid and hexosamine when compared to the ulcer-induced group. The mechanism of action of Musa sapientum is by stimulating the growth of the gastric mucosa by increasing mucosal protein i.e. sialic acid and hexosamine, which in turn increase the production of mucus and thus prevent erosion by the ulcer. These significant increased levels of sialic acid and hexosamine correlated with the increased mass of mucosa in the stomach of animals treated with banana. The mode of action of the banana appears to be unlike that of conventional anti-ulcerogenic drugs in that it promotes mucus secretion by stimulating the growth of mucosal cells The regenerated mucosa cells would rapidly seal damaged areas with a secretory layer of mucus and prevent further erosions due to gastric HCl and pepsin.[6]
The beneficial effect of the administration of dried banana powder might be due to its enhanced mucosal resistance. Musa sapientum also promotes healing of ulcers by the presence of water-soluble polysaccharides (e.g. Pectin) in unripe plantain banana.[27]
The level of NO was significantly elevated in the serum in ulcerated rats when compared to normal rats. Administration of Musa sapientum and antiulcer drugs decreases the level of NO in serum when compared to ulcerated rats. The level of NO in tissue was significantly reduced when compared to normal whereas treatment with Musa sapientum and antiulcer drugs brought the level of NO in tissue to near normal.
Nishida et al.,[28] in their study reported that NO produced by Constitutive Nitric Oxide Synthase (cNOS) is cytoprotective and NO produced by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is cytotoxic Tarek et al.,[29] in their study reported that the ulcerated rats exhibited marked reduction in tissue NO, which further adds to the enhanced neutrophil infiltration. It was reported that indomethacin caused up-regulation of endothelin-1[30] that leads to decreased production of gastric mucosal cNOS. In addition, the neutrophil-derived HOCl was reported to inhibit cytoprotective eNOS.[31] On the contrary, the study by Tarek et al.,[29] demonstrated that indomethacin produced a marked elevation in serum NO, the observed increase in myeloperoxidase MPO activity may facilitate the increase in serum NO as the MPO/H2O2 system serves as a major catalytic sink for NO preventing NO feedback inhibition.[32] Tarek et al.,[29] in their results reported that indomethacin-induced gastric injury might be mediated, at least in part, by the reduction in tissue cNOS-derived NO content and enhanced production of iNOS-derived NO in serum. Our findings concerning NO are in agreement with the widely accepted fact that, in the digestive system, NO produced by cNOS is cytoprotective and NO produced by iNOS is cytotoxic.
The antiulcer property of herbal plants has been studied and reported by many ethanobotanists.[33�C36] But studies by Ratnasooriya[37] and Arambewela et al.,[38] reported that even nutraceautical products like black tea and the ginger family have antiulcer property.
Vimal et al.,[39] in their studies with polyherbal drugs with the composition of Asparagus racemosus Wild (AR), Centella asiatica Linn (CA). Convolvulus pluricaulis (CP), Emblica officinalis (EO), Ocimum sanctum (OS) and Withania somnifera Dunal (WS), reported that the polyphenols, flavonoids etc., present in these plants have antiulcer activity. The possible mechanism of antiulcer activity may be by the presence of polyphenols in poly herbal drug which inhibited acetylcholine synthesis. Free radicals are involved in the progression of ulcers. Extract from Cassia auriculata possesses maximum in vitro free radical scavenging activity along with an ameliorative effect on various ulcerative parameters.[40]
Musa sapientum being a nutraceautical, can be consumed as food rather than as a drug which enhances the satiety value for the patients.
CONCLUSION
Our results showed protective effects against indomethacin-induced gastric erosions in animal models by Musa sapientum as shown by the absence of mucosal damage at the dosage of 100 mg/kg/ day. The active components such as leucocyanidin may be responsible for the antiulcer properties and protect the mucosa by stimulation of cell proliferation, promoting mucus secretion, increasing mucus resistance, inhibiting the Hcl secretion and thus healing the ulcer.Indigenous anti-ulcer activity of Musa sapientum on peptic ulcer
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249781/��
��
Pectin & Digestion | Healthfully
Aug 14, 2017 �� According to "The New Healing Herbs," pectin works with natural intestinal bacteria, or good bacteria, which turns the fiber into a soothing coating for irritated intestinal walls. The book also states that apple pectin has been found to counteract bacteria that causes diarrhea, such as Salmonella, E.Coli, and staphylococcus.
��
Regulatory Roles of Pectin Oligosaccharides on ...
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/mnfr.201801363The prebiotic regulation of the gut microbiota is a promising strategy to induce protective humoral and mucosal immune responses. The potential immune�\improving effects of pectin oligosaccharides (POS) in healthy mice and the potential mechanism mediated by specific intestinal bacteria are investigated.
��
��
��
Apple-Derived Pectin Modulates Gut Microbiota, Improves ...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808856Feb 29, 2016 �� Apple-derived pectin is the main soluble fiber in apples and can be fermented by gut microbiota in the colon to produce metabolites with local intestinal and systemic effects. Apple-derived pectin may also help to maintain the balance of gut microbiota [ 36 ].
����
��
Ripe vs. Unripe Bananas: Which are Better for You? - One ...
unripe bananas Benefits: One benefit of green bananas is the high resistant starch content . For anyone trying to avoid food with high sugar content, green bananas are an option whereas yellow ...
��
Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits of Green Bananas ...
Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits of Green Bananas. Although ripe bananas taste better, raw bananascan increase the rate of fat burning. This NutriNeat article describes how the nutritional elements present in green bananas promote weight loss and improve overall health.
The Effectiveness Of Bananas In Treating Diarrhea
Aug 10, 2017 �� Have Raw Bananas Boiled. Cook a couple of unripe bananas in boiling water with their skin on for 7 to 10 minutes. Remove the skin, mash up the bananas, add a bit of salt and butter, and have this twice a day. About 180�C200 g of cooked green bananas (about one and a half banana) per day seems to be effective for children. 17
��
Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits of Green Bananas ...
https://nutrineat.com/nutritional-facts-health-benefits-of-green-bananas
Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits of Green Bananas. Although ripe bananas taste better, raw bananas can increase the rate of fat burning. This NutriNeat article describes how the nutritional elements present in green bananas promote weight loss and improve overall health.
The Effectiveness Of Bananas In Treating Diarrhea
https://www.curejoy.com/content/bananas-good-diarrhea
Aug 10, 2017 �� Have Raw Bananas Boiled. Cook a couple of unripe bananas in boiling water with their skin on for 7 to 10 minutes. Remove the skin, mash up the bananas, add a bit of salt and butter, and have this twice a day. About 180�C200 g of cooked green bananas (about one and a half banana) per day seems to be effective for children. 17��
Green Banana Nutrition Facts
Raw Banana, Serving Size: 100 g
Water 74.91 g
Calories 89 kcal
Protein 1.09 g
Total lipid (fat) 0.33 g
Carbohydrate 22.84 g
Total Dietary Fiber 2.6 g
Total Sugars 12.23 g
Minerals
Calcium 5 mg
Iron 0.26 mg
Magnesium 27 mg
Phosphorus 22 mg
Potassium 358 mg
Sodium 1 mg
Zinc 0.15 mg
Vitamins
Vitamin C 8.7 mg
Thiamin 0.031 mg
Riboflavin 0.073 mg
Niacin 0.665 mg
Vitamin B6 0.367 mg
Folate 20 µg
Vitamin A, RAE 3 µg
Vitamin A, IU 64 IU
Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) 0.10 mg
Vitamin K 0.5 µg
Lipids
Total Saturated Fatty Acids 0.112 g
Total Monounsaturated Fatty Acids 0.032 g
Total Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids 0.073 g
Health Benefits of Resistant Starch
One medium, peeled, raw (slightly green) banana contains 4.7 g of resistant starch called RS2. As the name suggests, it resists digestion in the small intestine, and passes through the large intestine. There, it works like dietary fiber, and offers some of the benefits of both insoluble and soluble fiber. It helps maintain colon health, thus improving digestive health. The recommended daily intake of resistant starch is 20 grams, and 1 lb bag of green banana flour contains around 175 g of RS2.
✦ Unripe bananas, being rich in resistant starch, don��t lead to abnormal rise in blood sugar levels. The starch helps maintain normal blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity in both healthy and diabetic individuals. It improves insulin secretion in insulin resistant adults. Animal studies show that the starch can help improve the glycemic health of a baby if the mother consumes it during pregnancy.
✦ Green bananas don��t trigger hunger. As they keep one satiated, they help reduce appetite, which is essential if you want to lose weight.✦ Moreover, the starch promotes release of the hormone glucagon, which encourages fast burning of fat. Studies suggest that it also prevents weight regain in high fat diets.
✦ It helps reduce the symptoms of diarrhea.
✦ It acts like a mild laxative and helps maintain ��regularity��. It promotes the growth of healthy bacteria in the bowels, and this increased bacterial mass is responsible for bulking effects.
✦ The starch exhibits anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory properties which help prevent colon cancer (colorectal cancer). It works great for ulcerative colitis too.
✦ Animal studies show that the starch helps maintain eye health as well.
✦ When high glycemic starch and resistant starch were fed to two groups of aged animals, the animals who were fed resistant starch showed improved motor coordination and increased food intake after fasting.
✦ The starch, when consumed in sufficient amount, raises the level of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) which nourish the cells in the lining of the small intestine. This promotes more mineral absorption, especially calcium and magnesium.
✦ When included in a meal, it ensures less fat storage after that meal. Slow digestion means slow absorption of calories. Thus, it helps maintain the weight within normal range.
✦ It promotes low cholesterol and low triglyceride levels.
✦ It reduces the chances of having gallstones and kidney stones.Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits of Green Bananas - Nutrineat
https://nutrineat.com/nutritional-facts-health-benefits-of-green-bananas��
��
.png)