¡¡
CONTROVERSIES ON NORVALINE(VALINE)
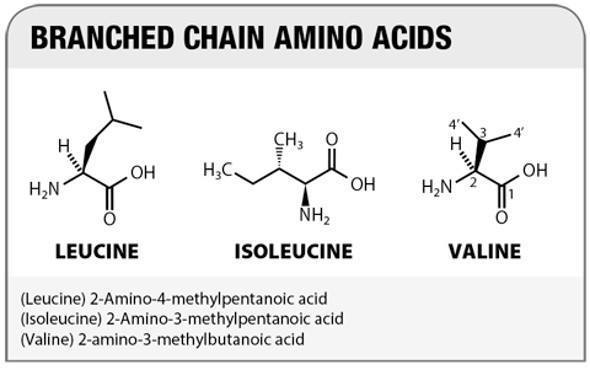
1. BCAA VALINE LINKED TO OBESITY AND DIABETES!
2. L-Norvaline, a new therapeutic agent against Alzheimer¡¯s disease (in animal models)
3. BCAA VALINE LINKED TO OBESITY AND DIABETES! L-NORVALINE CAN BE TOXIC TO THE BRAIN!
¡¡
Role of the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other metabolic disorders
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7059578/¡¡
Neural Regen Res. 2019 Sep; 14(9): 1562¨C1572.
L-Norvaline, a new therapeutic agent against Alzheimer¡¯s disease
Baruh Polis, MD,1,2* Kolluru D. Srikanth,2 Vyacheslav Gurevich,3 Hava Gil-Henn,2 and Abraham O. Samson1
1Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel
2Laboratory of Cell Migration and Invasion, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel
3Laboratory of Cancer Personalized Medicine and Diagnostic Genomics, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel
*Correspondence to: Baruh Polis, moc.liamg@silophurab.
Author contributions: Study design: BP, AOS; experiment implementation and data analysis: BP; western blotting: KDS; RT-PCR: VG; experiment advising and supervising: HGH; manuscript writing: BP; manuscript editing: AOS and HGH.
Abstract
Growing evidence highlights the role of arginase activity in the manifestation of Alzheimer¡¯s disease (AD). Upregulation of arginase was shown to contribute to neurodegeneration. Regulation of arginase activity appears to be a promising approach for interfering with the pathogenesis of AD. Therefore, the enzyme represents a novel therapeutic target. In this study, we administered an arginase inhibitor, L-norvaline (250 mg/L), for 2.5 months to a triple-transgenic model (3¡ÁTg-AD) harboring PS1M146V, APPSwe, and tauP301L transgenes. Then, the neuroprotective effects of L-norvaline were evaluated using immunohistochemistry, proteomics, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays. Finally, we identified the biological pathways activated by the treatment. Remarkably, L-norvaline treatment reverses the cognitive decline in AD mice. The treatment is neuroprotective as indicated by reduced beta-amyloidosis, alleviated microgliosis, and reduced tumor necrosis factor transcription levels. Moreover, elevated levels of neuroplasticity related postsynaptic density protein 95 were detected in the hippocampi of mice treated with L-norvaline. Furthermore, we disclosed several biological pathways, which were involved in cell survival and neuroplasticity and were activated by the treatment. Through these modes of action, L-norvaline has the potential to improve the symptoms of AD and even interferes with its pathogenesis. As such, L-norvaline is a promising neuroprotective molecule that might be tailored for the treatment of a range of neurodegenerative disorders. The study was approved by the Bar-Ilan University Animal Care and Use Committee (approval No. 82-10-2017) on October 1, 2017.
Keywords: dementia, arginase inhibition, arginine, urea cycle, microgliosis, neuroinflammation, cytokines, tumor necrosis factor, mTOR, neurodegenerationL-Norvaline, a new therapeutic agent against Alzheimer¡¯s disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6557086/¡¡
Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 18;20(18). pii: E4616. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184616.
Norvaline Restores the BBB Integrity in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.
Polis B1, Gurevich V2, Assa M3, Samson AO4.
Author information
1 Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed 1311502, Israel. baruhpolis@gmail.com.
2 Laboratory of Cancer Personalized Medicine and Diagnostic Genomics, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed 1311502, Israel. slavagur13@gmail.com.
3 Inter-laboratory Equipment Center, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed 1311502, Israel. michael.assa@biu.ac.il.
4 Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed 1311502, Israel. avraham.samson@biu.ac.il.
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder and the leading cause of dementia. The disease progression is associated with the build-up of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. However, besides the well-defined lesions, the AD-related pathology includes neuroinflammation, compromised energy metabolism, and chronic oxidative stress. Likewise, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction is suggested to be a cause and AD consequence.Accordingly, therapeutic targeting of the compromised BBB is a promising disease-modifying approach. We utilized a homozygous triple-transgenic mouse model of AD (3¡ÁTg-AD) to assess the effects of L-norvaline on BBB integrity. We scrutinized the perivascular astrocytes and macrophages by measuring the immunopositive profiles in relation to the presence of ¦Â-amyloid and compare the results with those found in wild-type animals. Typically, 3¡ÁTg-AD mice display astroglia cytoskeletal atrophy, associated with the deposition of ¦Â-amyloid in the endothelia, and declining nitric oxide synthase (NOS) levels. L-norvaline escalated NOS levels, then reduced rates of BBB permeability, amyloid angiopathy, microgliosis, and astrodegeneration, which suggests AD treatment agent efficacy. Moreover, results undergird the roles of astrodegeneration and microgliosis in AD-associated BBB dysfunction and progressive cognitive impairment.
L-norvaline self-evidently interferes with AD pathogenesis and presents a potent remedy for angiopathies and neurodegenerative disorders intervention.
KEYWORDS:
Alzheimer¡¯s disease; BBB; NO; NOS; angiopathy; arginase; arginine; norvalineNorvaline Restores the BBB Integrity in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. - PubMed - NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31540372¡¡
Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Oct;15(4):1036-1054. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0669-5.
L-Norvaline Reverses Cognitive Decline and Synaptic Loss in a Murine Model of Alzheimer's Disease.
Polis B1,2, Srikanth KD3,4, Elliott E4, Gil-Henn H3, Samson AO5.
Author information
Abstract
The urea cycle is strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Arginase-I (ARGI) accumulation at sites of amyloid-beta (A¦Â) deposition is associated with L-arginine deprivation and neurodegeneration. An interaction between the arginase II (ARGII) and mTOR-ribosomal protein S6 kinase ¦Â-1 (S6K1) pathways promotes inflammation and oxidative stress.In this study, we treated triple-transgenic (3¡ÁTg) mice exhibiting increased S6K1 activity and wild-type (WT) mice with L-norvaline, which inhibits both arginase and S6K1. The acquisition of spatial memory was significantly improved in the treated 3¡ÁTg mice, and the improvement was associated with a substantial reduction in microgliosis. In these mice, increases in the density of dendritic spines and expression levels of neuroplasticity-related proteins were followed by a decline in the levels of A¦Â toxic oligomeric and fibrillar species in the hippocampus. The findings point to an association of local A¦Â-driven and immune-mediated responses with altered L-arginine metabolism, and they suggest that arginase and S6K1 inhibition by L-norvaline may delay the progression of AD.
KEYWORDS:
Alzheimer¡¯s disease; L-arginine; L-norvaline; arginase; mTOR.; ribosomal protein S6 kinase ¦Â-1L-Norvaline Reverses Cognitive Decline and Synaptic Loss in a Murine Model of Alzheimer's Disease. - PubMed - NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30288668¡¡
Neural Regen Res. 2020 Aug;15(8):1460-1470. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.274328.
Role of the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other metabolic disorders.
Polis B1, Samson AO1.
Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel.
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease is an incurable chronic neurodegenerative disorder and the leading cause of dementia, imposing a growing economic burden upon society. The disease progression is associated with gradual deposition of amyloid plaques and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles within the brain parenchyma, yet severe dementia is the culminating phase of the enduring pathology. Converging evidence suggests that Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive decline is the outcome of an extremely complex and persistent pathophysiological process. The disease is characterized by distinctive abnormalities apparent at systemic, histological, macromolecular, and biochemical levels. Moreover, besides the well-defined and self-evident characteristic profuse neurofibrillary tangles, dystrophic neurites, and amyloid-beta deposits, the Alzheimer's disease-associated pathology includes neuroinflammation, substantial neuronal loss, apoptosis, extensive DNA damage, considerable mitochondrial malfunction, compromised energy metabolism, and chronic oxidative stress. Likewise, distinctive metabolic dysfunction has been named a leading cause and a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease that is apparent decades prior to disease manifestation.State-of-the-art metabolomics studies demonstrate that altered branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) metabolism accompanies Alzheimer's disease development. Lower plasma valine levels are correlated with accelerated cognitive decline, and, conversely, an increase in valine concentration is associated with reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease. Additionally, a clear BCAAs-related metabolic signature has been identified in subjects with obesity, diabetes, and atherosclerosis.
Also, arginine metabolism is dramatically altered in Alzheimer's disease human brains and animal models. Accordingly, a potential role of the urea cycle in the Alzheimer's disease development has been hypothesized, and preclinical studies utilizing intervention in the urea cycle and/or BCAAs metabolism have demonstrated clinical potential. Continual failures to offer a competent treatment strategy directed against amyloid-beta or Tau proteins-related lesions, which could face all challenges of the multifaceted Alzheimer's disease pathology, led to the hypothesis that hyperphosphorylated Tau and deposited amyloid-beta proteins are just hallmarks or epiphenomena, but not the ultimate causes of Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, approaches targeting amyloid-beta or Tau are not adequate to cure the disease. Accordingly, the modern scientific vision of Alzheimer's disease etiology and pathogenesis must reach beyond the hallmarks, and look for alternative strategies and areas of research.
KEYWORDS:
BCAAs; arginase; arginine; branched-chain aminotransferase; dementia; mTOR; norvaline; urea cycle; valine
PMID: 31997805 PMCID: PMC7059578 DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.274328
Free PMC ArticleRole of the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other metabolic disorders. - PubMed - NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31997805¡¡
A New Perspective on Alzheimer¡¯s Disease as a Brain Expression of a Complex Metabolic Disorder.
AuthorsPolis B2, Samson AO2.
EditorsIn: Wisniewski T1, editor. SourceAlzheimer¡¯s Disease [Internet]. Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications; 2019 Dec. Chapter 1.
Author information
1 New York University Alzheimer¡¯s Disease Center, New York University School of Medicine, New York, USA
2 Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel
Excerpt
Alzheimer¡¯s disease (AD) is an irredeemable chronic neurodegenerative disorder and the predominant cause of dementia. The disease progression is associated with the deposition of amyloid plaques and formation of neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, yet clinical dementia is the end and culminating stage of the enduring pathology. Recent evidence suggests that AD is characterized by distinctive abnormalities apparent on systemic, histological, macromolecular, and biochemical levels.Besides the well-described characteristic profuse neurofibrillary tangles, dystrophic neurites, and A¦Â deposits, the AD pathology includes substantial neuronal loss, inflammation, extensive DNA damage, considerable mitochondrial malfunction, impaired energy metabolism, and chronic oxidative stress.
Moreover, severe metabolic dysfunction leading to oxidative stress is a possible cause and hallmark of AD that is apparent decades before the disease manifestation. State-of-the-art metabolomics studies have proved that arginine and branched-chain amino acids metabolism disturbances accompany AD and contribute to its pathogenesis.
Repetitive failures to find an efficient anti-amyloid or anti-Tau treatment, which would face the challenges of the complex AD pathology, led to the hypothesis that hyperphosphorylated Tau and deposited A¦Â proteins are hallmarks, not the ultimate causes of AD. Accordingly, the modern scientific vision of AD etiology and pathogenesis must reach beyond the hallmarks and look for alternative strategies and areas of research.
Copyright: The Authors.
Sections
INTRODUCTION
EARLY- AND LATE-ONSET AD ARE TWO DIFFERENT ENTITIES
LOAD AS A SYSTEMIC METABOLIC DISORDER
A CONTRIBUTION OF THE UREA CYCLE AND POLYAMINE METABOLIC PATHWAY IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF AD
A PUTATIVE ROLE OF BCCAS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF AD
CONCLUSION
REFERENCESA New Perspective on Alzheimer¡¯s Disease as a Brain Expression of a Complex Metabolic Disorder - PubMed - NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31895518¡¡
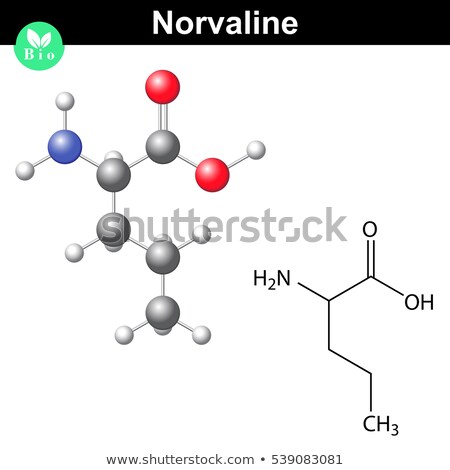
Ingredients: Norvaline
Team Suppreviewers
November 1, 2017
No Comments
The History & Background of Norvaline
Type:Amino Acid
Potency: 8/10
Norvaline is a water dissolvable amino acid which is an isomer of the spread chain amino acid (BCAA), Valine. Isomers are basically atoms with a similar concoction sythesis yet unique structure. Norvaline is a typical fixing in pre exercise supplements on account of their capacity to help enhanced blood stream and accordingly the pump. Pre-exercises utilize arginine and different mixes to enlarge veins and create nitric oxide, which surges muscle tissue with additional blood, oxygen, and supplements for development. This is what¡¯s ordinarily known as an exercise ¡°pump,¡± and it gives you a sentiment additional power and vitality.
Norvaline is said to be discovered normally in nourishments, for example, meats, dairy, grains, vegetables and nuts. Supplemental Norvaline is delivered artificially; be that as it may it can likewise be created by microscopic organisms, for example, E. coli, which is frequently present in the ordinary greenery of the gut.
Use in Supplements
Norvaline¡¯s capacity to increment endogenous levels of arginine is the reason it is frequently found in pre exercise supplements. Arginine increments nitric oxide levels in the body, which can help blood stream around the body. This can supply our muscles with key oxygen and supplements to help profit execution and preparing.
Norvaline can likewise help bolster the ¡®Pump¡¯, which is a much looked for after restorative impact of utilizing some pre exercise supplements. Pre-exercises utilize arginine and different mixes to enlarge veins and create nitric oxide, which surges muscle tissue with additional blood, oxygen, and supplements for development.
Common Dosing
In case you¡¯re utilizing L-norvaline as a remain solitary supplement or need to add somewhat more to your item stack, specialists prescribe in the vicinity of 100 and 200 mg for most extreme safe outcomes.
Products Containing Norvaline
Potential Side Effects of Norvaline
Norvaline is a great compound however users us to be aware of its side effects such as dizziness, nausea, fatigue and lightheadedness. Normally it has no side effects for people who don¡¯t suffer from any blood pressure problems, if you happen to have this it is better to talk to your doctor before taking any supplements with norvaline on it.
FAQs
WHAT DOES IT DO?
The majority of supplements featuring L-norvaline is pre-workouts and ¡°pump¡± boosters claimed to increase intra-workout power and recovery.
These pre-workouts typically use large amounts of arginine to relax blood vessels and stimulate nitric oxide production, flooding muscles with oxygen and nutrients. The result is a massive muscle pump that gives you more energy and provides for better recovery.
Nitric oxide is the real key here. It¡¯s what provides the burst of blood and nutrient flow. No nitric oxide, no pump. This is where L-norvaline comes in.
DOES IT AFFECT MUSCLE?
Because it¡¯s an analog of valine, many people think L-norvaline also contributes to muscle growth. This is a misconception; L-norvaline is not used by the body to create muscle tissue.
However, just because it doesn¡¯t contribute directly doesn¡¯t mean L-norvaline is useless for growth. By extending pump length and intensity, L-norvaline provides muscle tissue with massive amounts of oxygen and nutrients, including other amino acids.
While you¡¯ll notice the extra power during workouts, this extended pump has also been shown to dramatically reduce soreness and post-exercise recovery time.
SHOULD I USE L-NORVALINE?
As previously covered, for most people L-norvaline is nothing but good news. It¡¯s backed by great studies and is a safe way to improve exercise performance. However, those with pre-existing conditions need to be aware of possible side effects.
Studies
Norvaline is a simple of the amino acid L-valine. Research demonstrates that L-norvaline is a solid inhibitor of arginase movement due to its auxiliary similitude to ornithine, which causes a criticism control on the action of arginase. When you hinder arginase, NO is delivered consistently at a higher rate within the sight of NOS and satisfactory L-arginine. L-arginine is the restricting component for NO generation from NOS, so hindering the arginase protein successfully expands the creation of NO by as much as 60%.
Regardless, urea¡¯s hindrance brings about the powerlessness to legitimately exchange nitrogen from glutamine to urea, bringing about the aggregation of nitrogenous waste. The drawn out restraint of urea creation inside the liver could possibly prompt alkali lethality (hyperammonemia). The brokenness of these natural components could bring about liver disappointment, neurotoxicity, cerebral edema, and could make negative harm the Central Nervous System, and could at last outcome in death.
Final Review of Norvaline
Norvaline is a pre-exercise pump or promoter which works fundamentally by expanding nitric oxide creation in the human body. It is among the run of changed extended amino acids which are encouraged to be taken through natural supplementation for having been considered upon over the most recent quite a long while. Norvaline is a successful answer for muscle improvement. Through this supplementation, exercise endeavors will be expanded for long haul practice without fatigue.The Amazing Benefits of Norvaline
https://www.suppreviewers.com/ingredients/norvaline/¡¡
Neural Regen Res. 2020 Aug; 15(8): 1460¨C1470.
Role of the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other metabolic disorders
Baruh Polis, MD* and Abraham O. Samson
Drug Discovery Laboratory, The Azrieli Faculty of Medicine, Bar-Ilan University, Safed, Israel
Abstract
Alzheimer¡¯s disease is an incurable chronic neurodegenerative disorder and the leading cause of dementia, imposing a growing economic burden upon society. The disease progression is associated with gradual deposition of amyloid plaques and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles within the brain parenchyma, yet severe dementia is the culminating phase of the enduring pathology. Converging evidence suggests that Alzheimer¡¯s disease-related cognitive decline is the outcome of an extremely complex and persistent pathophysiological process.The disease is characterized by distinctive abnormalities apparent at systemic, histological, macromolecular, and biochemical levels. Moreover, besides the well-defined and self-evident characteristic profuse neurofibrillary tangles, dystrophic neurites, and amyloid-beta deposits, the Alzheimer¡¯s disease-associated pathology includes neuroinflammation, substantial neuronal loss, apoptosis, extensive DNA damage, considerable mitochondrial malfunction, compromised energy metabolism, and chronic oxidative stress. Likewise, distinctive metabolic dysfunction has been named a leading cause and a hallmark of Alzheimer¡¯s disease that is apparent decades prior to disease manifestation.
State-of-the-art metabolomics studies demonstrate that altered branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) metabolism accompanies Alzheimer¡¯s disease development. Lower plasma valine levels are correlated with accelerated cognitive decline, and, conversely, an increase in valine concentration is associated with reduced risk of Alzheimer¡¯s disease. Additionally, a clear BCAAs-related metabolic signature has been identified in subjects with obesity, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Also, arginine metabolism is dramatically altered in Alzheimer¡¯s disease human brains and animal models.
Accordingly, a potential role of the urea cycle in the Alzheimer¡¯s disease development has been hypothesized, and preclinical studies utilizing intervention in the urea cycle and/or BCAAs metabolism have demonstrated clinical potential. Continual failures to offer a competent treatment strategy directed against amyloid-beta or Tau proteins-related lesions, which could face all challenges of the multifaceted Alzheimer¡¯s disease pathology, led to the hypothesis that hyperphosphorylated Tau and deposited amyloid-beta proteins are just hallmarks or epiphenomena, but not the ultimate causes of Alzheimer¡¯s disease.
Therefore, approaches targeting amyloid-beta or Tau are not adequate to cure the disease. Accordingly, the modern scientific vision of Alzheimer¡¯s disease etiology and pathogenesis must reach beyond the hallmarks, and look for alternative strategies and areas of research.
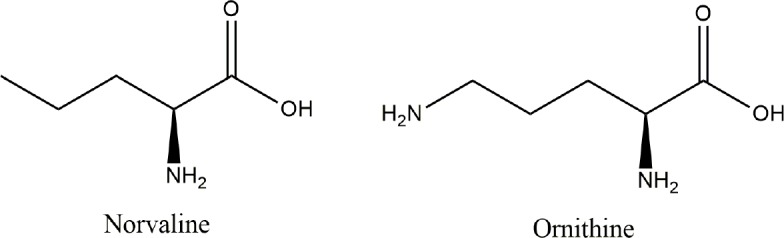
Structural similarity with ornithine (Figure 7) provides the substance with properties of negative feedback arginase inhibition (Polis and Samson, 2018). Suppressing arginase activity has been suggested to decrease the risk and frequency of cardiovascular diseases (Pernow and Jung, 2013). Accordingly, various arginase inhibitors have been intensively investigated in rodent models and in humans. In this context, norvaline¡ªa non-competitive arginase inhibitor¡ªhas attracted serious interest.
As an arginase inhibitor, norvaline has been shown to improve available resources of arginine and to increase nitric oxide (NO) production. These features support the normal endothelial function (Ming et al., 2009). Consequently, norvaline given for 7 days in a dose of 10 mg/kg/day has been shown to prevent the development of systemic endothelial dysfunctions in L-NAME and methionine-induced NO deficiency in rats (Pokrovskiy et al., 2011). In one study, diabetic rats treated with 50 mg/kg of norvaline for 6 weeks demonstrated alleviated hypertension via a mechanism involving the protection of endothelial-dependent relaxation and NO generation (El-Bassossy et al., 2012). Gilinsky et al. (2019) recently showed that norvaline effectively reduces blood pressure and induces diuresis in rats with inherited stress-induced arterial hypertension without any effect on wild-type animals. Also, the administration of norvaline (10 mg/kg) for 1 month significantly improved serum nitrates, urea, LDH, testosterone, and testicular protein levels in diabetic rats. Moreover, the treated animals demonstrated enhanced sperm motility and viability (De et al., 2016). The same group of scientists discovered a potential mechanism of norvaline induced phenotype and found a positive effect on scavenging free radicals and on increasing the levels of antioxidant enzymes in rat testes (De and Singh, 2016).
Recent translational research on norvaline has demonstrated its many properties in applications relating to an extensive spectrum of metabolic diseases, including AD. Remarkably, the substance interferes with all major aspects of AD pathogenesis, which makes its use extremely attractive.
Keywords: arginase, arginine, branched-chain aminotransferase, BCAAs, dementia, mTOR, norvaline, urea cycle, valineRole of the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other metabolic disorders
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7059578/¡¡
Brian Turner Posted on February 08 2019
PLUS, BREAKING NEWS!
L-NORVALINE CAN BE TOXIC TO THE BRAIN!
By Steve Blechman
A most recent study published in the journal Metabolife (January 14, 2019) found a strong association between branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and the risk of incidents for type 2 diabetes in China. The branched-chain amino acid valine had the highest risk prediction of incidents of type 2 diabetes! These findings could aid in diabetes risk assessment in the Chinese and global population!
There¡¯s an overwhelming amount of evidence over the years that elevated branched-chain amino acids are associated with obesity and insulin resistance. A most recent meta-analysis study (Acta Diabetologica, November 9, 2018) found that oral BCAA elevates circulating dietary BCAA intake and were positively and inversely related to type 2 diabetes, mellitus and overweight/obesity risk respectively! The researchers said, ¡°Eight articles on randomized clinical trials of oral BCAA supplementation and seven articles on dietary BCAA intake and type 2 diabetes/obesity risks were eligible for inclusion in our meta-analysis.¡±
Research has shown that elevated levels of valine are present in the blood of diabetic rats, mice and humans (Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2014). When the mice were fed a diet without valine, insulin sensitivity improved after only one day. Mice on the valine-free diet lasting an entire week showed decreased blood glucose levels, indicating that there was improved insulin function (Metabolism, 2014). It was reported in the journal Nature Medicine in 2015 that valine catabolite 3-hydroxyisobutyrate (3-HIB) promoted the accumulation of fat within muscle tissue by directly stimulating fatty uptake in the muscle. The intramuscular fat activates certain signaling cascades within the muscle cell that diminish insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance. This study also found that inhibiting the production of 3-HIB prevented the uptake of fat. Other studies support the negative effect of 3-HIB on insulin signaling with elevated 3-HIB in the muscle of human subjects with diabetes (J Lipid Res, 1989; Diabetologia, 2015). An article titled Insulin Resistance, And What May Contribute To It by Lila Abassi and published on the American Council on Science and Health website on March 14, 2016 reported on ¡°¡ a study published in Nature Medicine, [that] scientists have discovered that 3-hydroxyisobutyrate (3-HIB), one of the intermediate products in the breakdown of the BCAA valine, plays a role in the transport of fatty acids into skeletal muscle cells, which creates fatty muscles ¡ª a contributor to insulin resistance.¡± Abassi also states, ¡°Thus far, it has been a relative mystery as to how BCAAs play a role in insulin resistance. Skeletal muscles display resistance to insulin when there is excess fat inside their cells.¡± In her closing of the article, Abassi said, ¡°What the researchers found was that 3-HIB acted as a shuttle in muscle cells, allowing blood vessels in skeletal muscle tissue to move fat into skeletal muscle. The more 3-HIB, the more fat was transported ¡ª and conversely, when scientists blocked 3-HIB from being made, there was less uptake of fat into skeletal muscle.¡±
In a most recent study in the journal Nutrients (January 5 2019, Nutrients) valine intake in 12 healthy lean men was not shown to be effective on weight loss, satiety or blood glucose levels. Unlike valine, leucine has been shown to improve blood glucose levels and insulin function.
Leucine consumption alone has been shown to rescue insulin-signaling deficiency (PLoS, 2011). A recent study (Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2018) found that oral administration of leucine improved endothelial function in healthy individuals when infused with glucose. Acute hyperglycemia impairs endothelial function in healthy individuals. This study found that leucine administration prevented hyperglycemia-mediated endothelial function. Unlike leucine, which avoids insulin resistance by increasing mitochondrial-driven fat loss, valine does not encourage mitochondrial biogenesis. ¡°Impaired mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle is one of the major predisposing factors to metabolic diseases, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease,¡± the study authors noted.
Leucine supplementation increases insulin sensitivity by activating SIRT1 activity. SIRT1 is known to ¡°promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative capacity and prevent the mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle¡± (Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2014). Leucine may also attenuate adiposity and promote weight loss during energy restriction (Nutrition 2006, Diabetes, 2007). These effects are in part by activating the SIRT1-dependent pathway, stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis and increased oxygen consumption (Nutrition Metabolism, 2008). Mitochondrial biogenesis and SIRT1 expression in skeletal muscle has also been shown to increase life span in middle-aged mice (Cell Metabolism, 2010). As far as isoleucine is concerned, unlike valine, it has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by increasing glucose into muscle cells (Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2007). Research has shown that leucine amplifies the effect of the diabetic drug metformin on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in diet-induced obesity. Adding leucine to metformin has been shown to be synergistic, enabling a 65% to 80% metformin reduction with no loss of diabetic efficacy and a 40% metformin dose reduction in a recent clinical trial (Diabetes, June 12, 2016; Metabolism 2016 and Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2018). Metformin has been approved by the FDA for over 25 years as an anti-diabetic drug and has recently been reviewed as a possible FDA-approved anti-aging drug. Recent research has also shown that metformin can lower elevated valine levels in diabetics.
¡°There's growing evidence to suggest that BCAAs isn't just a passive marker of diabetes but may actually play a role in driving the disease,¡± Gerszten said. ¡°It gives us the motivation to test whether changes in the amino acid intake in our diets would be worth exploring.¡±
It¡¯s clear based on scientific research that high-circulating BCAAs are associated with obesity and diabetes. The latest available literature has shown that the branched-chain amino acid valine (catabolite 3-HIB) is the probable cause!
It is my recommendation to take leucine by itself. The research shows that leucine is a powerful anabolic trigger and enhances protein synthesis and can promote muscle growth and recovery. Also, leucine supplementation can improve mitochondrial biogenesis and function, increase insulin sensitivity and may also enhance fat loss and improve lean body mass.
BREAKING NEWS!
L-NORVALINE CAN BE TOXIC TO THE BRAIN!
A recent report by ScienceDaily released on February 7, 2019 shows that the L-norvaline, used in many bodybuilding pre-workout supplements as a nitric oxide activator, could be bad for the brain! A study performed by the University of Technology in Sydney, Australia shows that L-norvaline may be linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Norvaline is an analog of the amino acid L-valine. Don¡¯t confuse norvaline with the amino acid L-valine. L-valine is an essential amino acid; norvaline is not.
One of the researchers, Kate Samardzic, spoke to ScienceDaily about the April 2019 article that appears in the journal Toxicology in Vitro.
"Some non-protein amino acids are toxic because they can mimic protein amino acids and deceive the body into making faulty proteins; a property used by some plants to kill predators.
"Some plants can even release non-protein amino acids into the soil to kill other plants so that they can have access to all the nutrients. Chemical warfare among plants is a well-known phenomenon. Since there was evidence that L-norvaline has antimicrobial and herbicidal activity we examined its toxicity in human cells," Samardzic said.
ScienceDaily also reported, ¡°This is the first study that investigates the toxicity of L-norvaline in human cells, specifically testing its effect on the health of brain cells arising from its ability to mimic protein amino acids.¡±
Associate Professor Ken Rodgers, who led the research, said the study revealed that L-norvaline, while it might initially allow cells to produce more energy, after a while the machinery of the cell that generates the energy is damaged. ¡°People are taking supplements such as this without really knowing much about what the long-term consequences might be,¡± Rodgers said.
The amino acid L-norvaline may cause damage to brain cells by reducing cell viability and induced necrotic cell death, increase mitochondrial fragmentation and bioenergetic dysfunction. Stick with proven safe and effective nitric oxide activators such as citrulline, citrulline malate, beetroot, grapeskin polyphenols and folic acid.BCAA VALINE LINKED TO OBESITY AND DIABETES!
https://advancedmolecularlabs.com/blogs/news/bcaa-valine-linked-to-obesity-and-diabetes¡¡
¡¡
¡¡