中国药科大学研究发现,生姜可以杀死人类白血病细胞
Ginger Kills Leukemia Cells, Found by China Pharmaceutical University
这是一个令人振奋的消息,姜烯酚,我们熟识的生姜的一种主要有效成分,被中国药科大学的研究人员发现可以杀死人类的转移性和原发性白血病细胞。
在这个发表在《分子肿瘤Molecular Cancer》(Molecular Cancer是一份开放访问,同行评审的在线杂志)上的研究中,研究人员发现,姜烯酚(6-Shogaol)在体外和体内都能诱导人白血病细胞凋亡(细胞死亡),而没有副作用!
值得注意的是,姜烯酚有选择性地对抗白血病细胞,而不对抗正常的骨髓单核细胞。
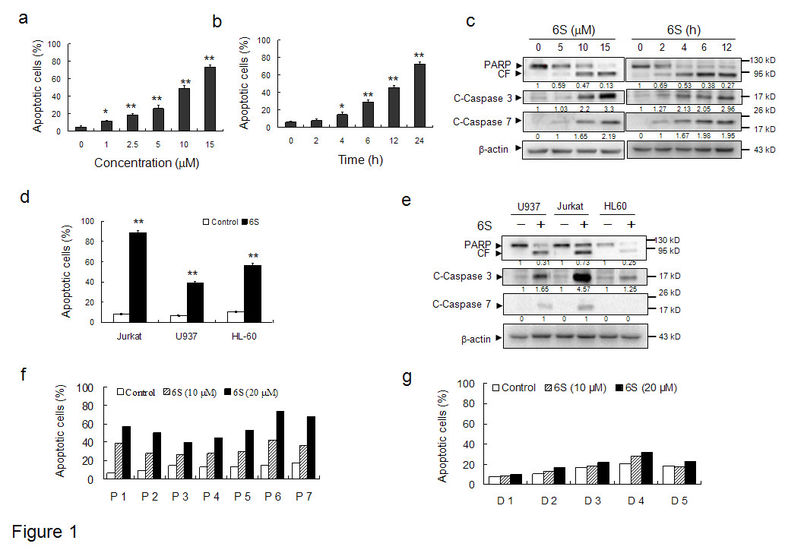
Figure 1
6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in transformed and primary leukemia cells. Cells apoptosis was determined using Annexin V/PI staining by flow cytometry. The values obtained from Annexin V/PI represent the mean±SD for three separate experiments. The difference were significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (a) Jurkat cells were treated without or with various concentrations of 6-shogaol (6S) for 24 h. (b) Jurkat cells were treated without or with 15 μM for different time intervals as indicated. (c) Jurkat cell were treated without or with 6S for various concentrations or time intervals as indicated, total cellular extracts were prepared and subjected to western blot assay using antibodies against PARP, cleaved-caspase 3 (C-Caspase 3) and cleaved-caspase 7 (C-Caspase 7). (d and e) Jurkat, U937, and HL-60 cells were treated without or with 15 μM for 24 h, after which apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry. Total cellular extracts of protein were prepared and subjected to western blot using antibodies as indicated. (f) Mononuclear cells were isolated from the peripheral blood of 7 patients with leukemia (designated as P1–7), including 4 AML, 1 MM (P7), and 2 CLL patients (P3 and P4). Cells were then treated without or with 10 and 20 μM 6S for 24 hours. (g) Mononuclear cells were isolated from the peripheral blood of 5 healthy donors and incubated with 0, 10 and 20 μM of 6S for 24 hours.
另外,沙特阿拉伯皇家大学,美国MICHIGAN大学,马来西亚国立大学,泰国清迈大学的研究表明,生姜可以诱导多种肿瘤细胞死亡,包括肺癌、结直肠癌、肝癌、卵巢癌, 前列腺癌和乳腺癌细胞。
关于生姜的现代研究的另一个令人欣喜的方面是,生姜中的单个化合物在一起服用时具有协同效应。换句话说,食用生姜最健康的方法可能是把它当作一种整体食物来食用,建议和含糖量低的水果和蔬菜一起榨汁,协同发挥更强大的抗肿瘤作用。
参考文献:
6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through a process involving caspase-mediated cleavage of eIF2α
Qun Liu†, Yong-Bo Peng†, Ping Zhou, Lian-Wen Qi, Mu Zhang, Ning GaoEmail author, E-Hu LiuEmail author and Ping Li
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-12-135



.png)