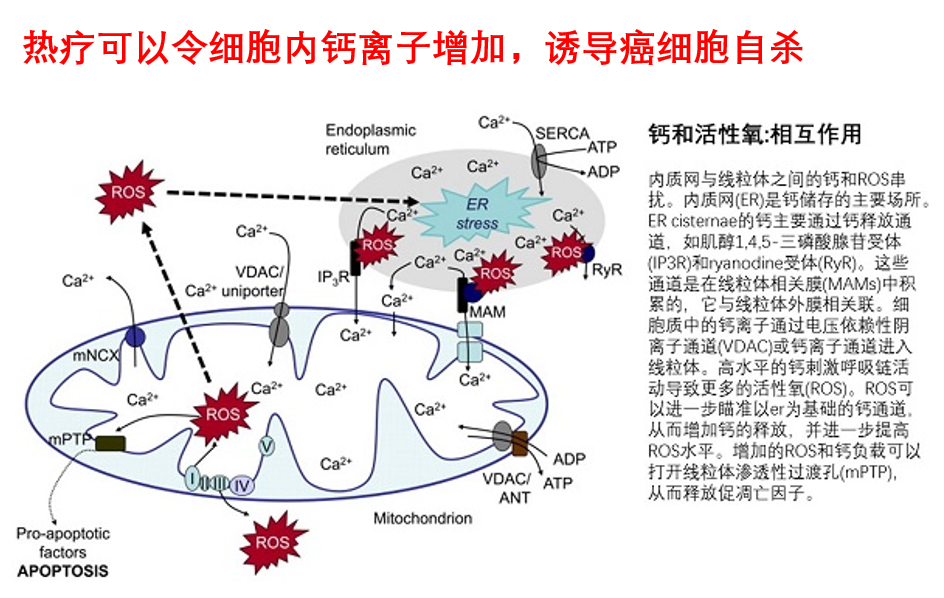
热疗可以令细胞内钙离子增加,诱导癌细胞自杀
细胞内钙离子(2+)在热疗引起的细胞凋亡中的作用及其在U937细胞中的作用
The role of intracellular Ca(2+) in apoptosis induced by hyperthermia and its enhancement by verapamil in U937 cells.
备注:U937细胞
在1974年,一名37岁男性患者的组织细胞淋巴瘤中分离出U937细胞。由于它们是表达许多单核细胞特性的少数细胞系之一,它们常常被用来研究单核细胞的行为和分化。U937细胞经粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(GM-CSF)治疗后凋亡;Okuma等人,2000),使它们成为研究凋亡细胞信号的有用模型。
目的:在U937细胞中,研究了42度C和44度C热疗引起的细胞凋亡和与verapamil的联合以及细胞内Ca(2+)浓度变化的关系。
方法:根据DNA片段、细胞核形态变化和磷脂酰丝氨酸在体外浆细胞膜上的表达,评估了热疗引起的细胞凋亡。用流式细胞术测定这些变化。通过使用Fura-2的数字图像分析技术监测热疗后单个细胞的[Ca(2+)]i。
结果:热疗诱导的细胞凋亡在6小时后到达高原,并被发现具有时间和温度依赖性。在30分钟后,DNA断裂的最大值为44摄氏度,Verapamil提高了正常细胞42度C和44摄氏度和耐热细胞中直到44摄氏度高温的细胞凋亡。在正常的和耐热的细胞中加入维拉帕米后,热疗使细胞内钙离子浓度(高于200nM)增加的细胞数目明显增加,Verapamil的加入在正常细胞和耐受细胞中,进一步增加钙离子的浓度。细胞内Ca(2+)螯合剂,BAPTA-AM,以剂量依赖性的方式显著降低了热疗引起的细胞凋亡。
结论:这些结果表明细胞内钙离子[Ca(2+)]i的增加在热疗和Verapamil联合治疗的正常和耐热U937细胞中起着至关重要的作用。此外,热疗联合药物治疗对癌症治疗具有潜在的意义。
https://s.click.taobao.com/hYsTINw
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001 Apr 1;49(5):1369-79.
The role of intracellular Ca(2+) in apoptosis induced by hyperthermia and its enhancement by verapamil in U937 cells.
Abstract
PURPOSE:
The relationship between apoptosis induced by 42 degrees C and 44 degrees C hyperthermia alone or in combination with verapamil and changes in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) was investigated in U937 cells. METHODS:
Apoptosis induced by hyperthermia was assessed according to DNA fragmentation, nuclear morphologic changes, and expression of phosphatidylserine on the outside plasma cell membrane. These changes were measured by flow cytometry. The [Ca(2+)]i of individual cells after hyperthermia was monitored by a digital image-analyzing technique using Fura-2. RESULTS:
Hyperthermia-induced apoptosis reached a plateau after 6 h and was found to be both time and temperature-dependent. DNA fragmentation was maximum at 44 degrees C after 30 min. Verapamil enhanced the apoptosis induced by 42 degrees C and 44 degrees C hyperthermia in normal cells and by 44 degrees C hyperthermia in thermotolerant cells. The number of cells containing higher [Ca(2+)]i (more than 200 nM) was significantly increased by hyperthermia and further elevated by the addition of verapamil in both normal and thermotolerant cells. Apoptosis induced by hyperthermia was markedly decreased by an intracellular Ca(2+) chelator, BAPTA-AM, in a dose-dependent manner. CONCLUSION:
These results indicate that [Ca(2+)]i increase plays a crucial role in apoptosis induced by hyperthermia and the combined treatment with verapamil in normal and thermotolerant U937 cells. Furthermore, hyperthermia-combined drug therapy has potential significance in cancer therapy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11286845
.png)

.png)
.png)